Selecting the right jib crane is only half the story. The true performance, safety, and ROI of your lifting system hinge on the quality and suitability of its jib crane components—from the boom and slewing mechanism to the hoist, trolley, controls, and end effectors. In this comprehensive guide, we break down the essentials so you can spec, buy, and maintain with confidence.
Want to dive deeper into outcomes? Read: How Can Jib Crane Components Enhance Productivity?
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are the Core Jib Crane Components?
Understanding how each part works—and how parts work together—is the foundation of smart selection.
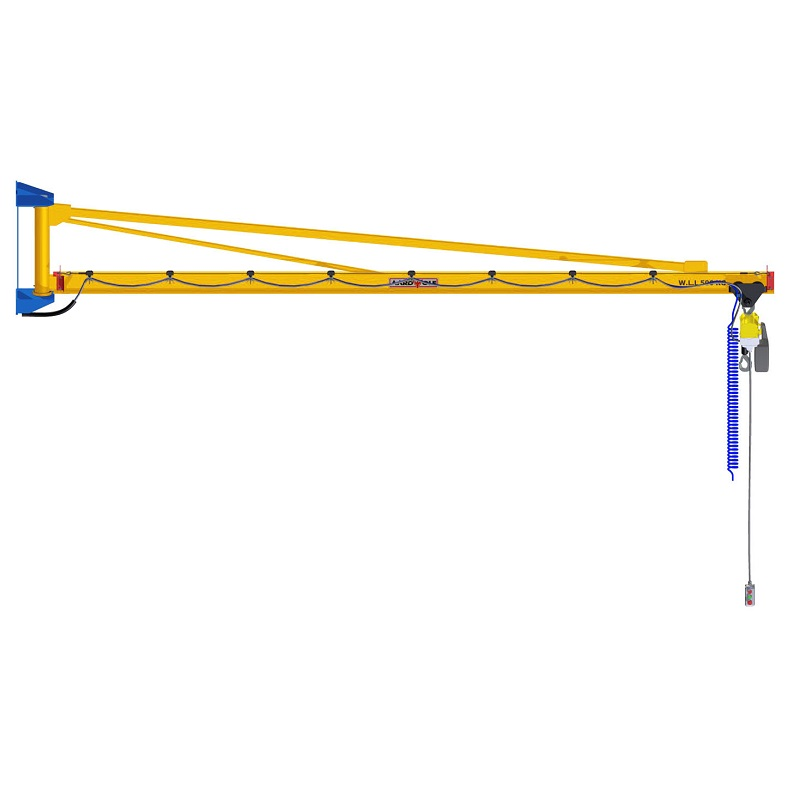
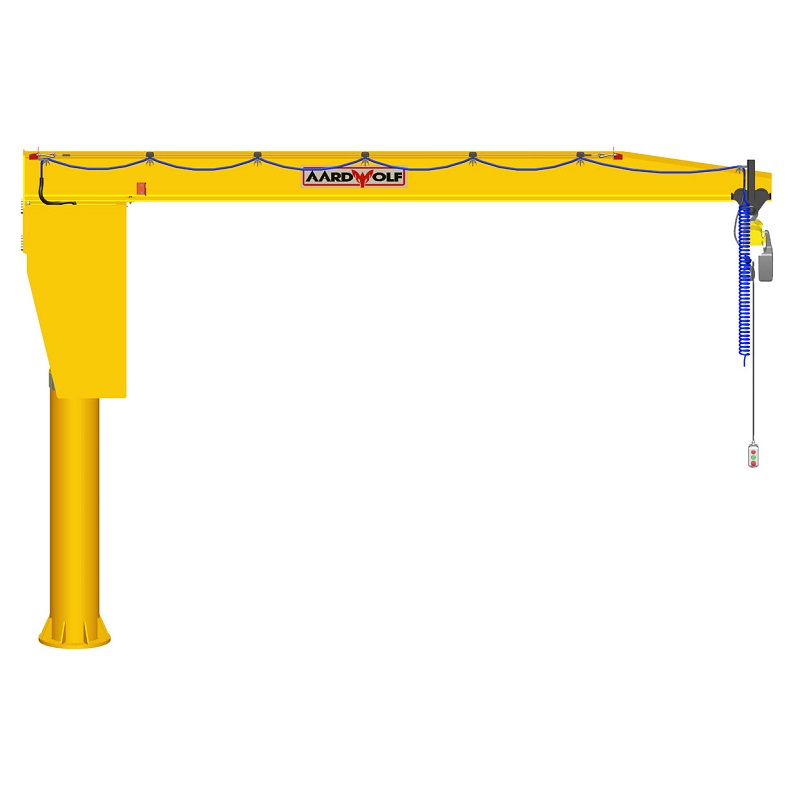
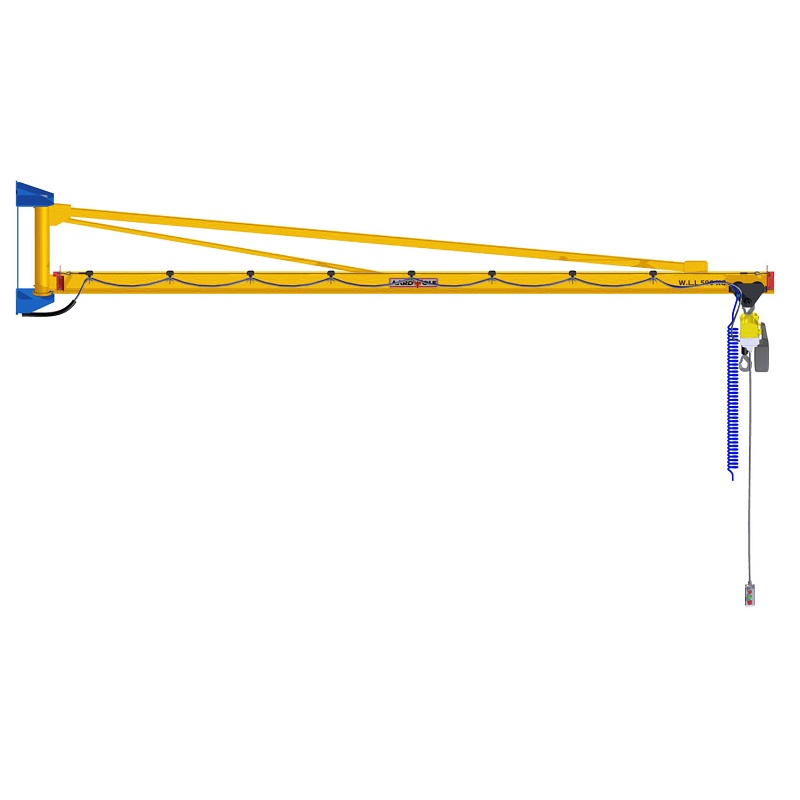
1) Boom (Jib Arm)
The horizontal member that carries the load, defined by reach (length) and under-boom clearance. Boom rigidity and construction (e.g., I-beam, boxed, or articulated segments) directly affect deflection, positioning accuracy, and usable headroom.
2) Mast/Column or Wall Bracket
The vertical support. Freestanding pillar jibs rely on a properly engineered base and anchors; wall-mounted variants attach to building steel or reinforced concrete. The support must be sized for torsion and shear induced by the slewing boom.
3) Slewing/Bearing & Rotation Stop
This is the rotation interface that enables the boom to swing. Designs range from plain bearings to roller slewing rings and powered slewing drives. Pay attention to:
- Slew torque and startup friction
- Lubrication access points
- Mechanical stops and travel limits
4) Trolley
Runs along the boom to position the hoist. The right trolley wheel material, flange profile, and load rating reduce track wear and improve smoothness. Consider low-headroom or short-radius trolleys when ceilings are tight.
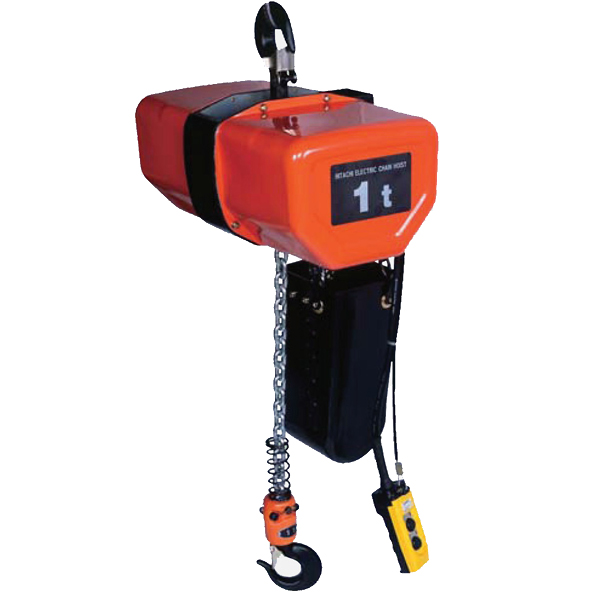
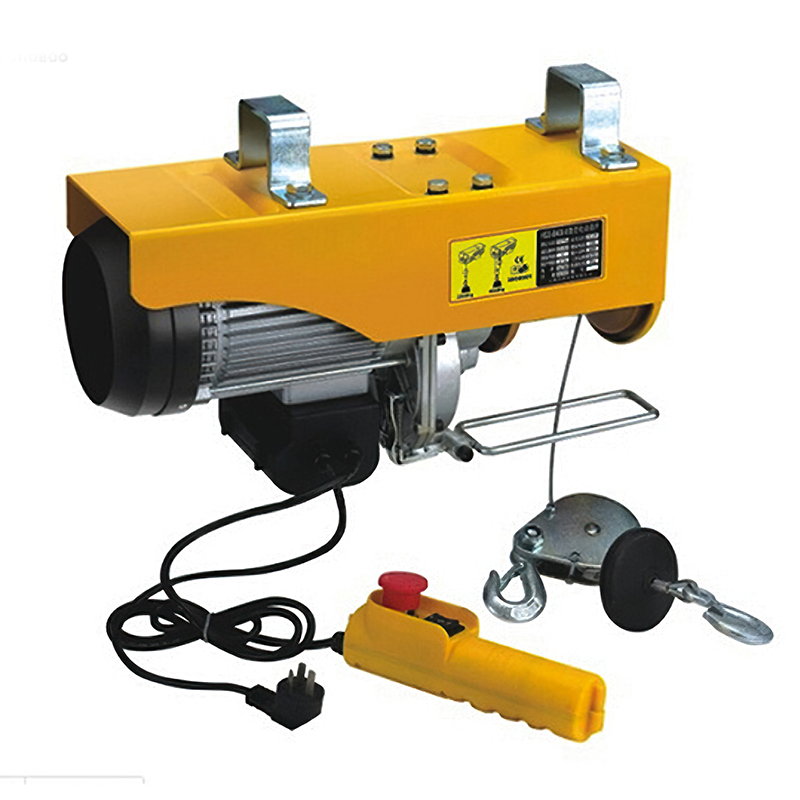
5) Hoist (Manual, Electric Chain, or Wire Rope)
The heart of vertical lifting. Correct duty class, lifting speed, controls, and reeving prevent premature wear and keep cycle times on target. In many light-to-medium-duty applications, an electric chain hoist balances cost, speed, and serviceability.
6) Lifting Attachment / End Effector
Where the load meets the crane—hooks, clamps, magnets, and vacuum lifters. Match attachment style to your material:
- For architectural glass and glazing, a dedicated glass lifter boosts safety and reduces handling damage.
- In stone, precast, and quarry operations, see block lifting strategies to protect edges and surfaces while improving throughput.
7) Controls & Power Feed
Pendant, radio remote, or smart controls influence ergonomics and safety. For powered slewing and trolleys, evaluate festoon systems, energy chains, or slip rings for clean cable management.
8) Safety Systems
Overload protection, upper/lower limit switches, emergency stop, thermal protection on motors, and torque limiters. Safety interlocks and zone limits mitigate collision risks.
Why Jib Crane Component Selection Is Business-Critical
Choosing the right jib crane components is not just an engineering exercise—it’s a strategic decision that shapes productivity, safety, and lifetime costs.
1) Performance & Throughput
- The boom geometry determines reach and coverage. Too short and you add wasteful secondary handling; too long and you risk deflection and overspec.
- Hoist speed and trolley responsiveness directly govern cycle time. Spec for your heaviest routine duty, not a one-off lift.
- End effectors tailored to the load (e.g., vacuum pads for glass, clamps for blocks) cut rework and breakage.
Explore the KPI ties in: How Can Jib Crane Components Enhance Productivity?
2) Operator Safety & Compliance
Right-sized brakes, verified load paths, reliable limits, and ergonomic controls protect your people and your accreditation. Thoughtful component pairing (e.g., soft-start drives, anti-sway features) reduces risk during precise placement.
For audit-ready checklists, see: What Role Do Jib Crane Components Play in Safety Checks?
3) Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Upfront savings disappear fast if a hoist is under-classed or a slewing bearing is inaccessible for lubrication. Spec with maintenance access, spares availability, and duty class in mind to extend service intervals and avoid unplanned downtime.
Matching Jib Crane Components to Your Application
By Mounting Style & Space Constraints
- Wall-Mounted Articulated Jibs: A smart fit for tight bays with obstacles, enabling knuckle-like motion for precise placement around corners or machines. See Articulated Jib Crane – Wall Mounted for space-optimized maneuverability.
- Freestanding (Column) Jibs: Maximum coverage without relying on building steel. Ideal when floor layout changes or when wall loads are restricted.
By Load & Duty Profile
- Intermittent, Light Loads: Manual or basic electric hoists with pendant controls may suffice.
- High-Cycle, Medium Loads: Electric chain hoists with dual-speed or VFD, robust trolley, and powered slewing.
- Heavy or Abrasive Environments: Consider sealed slewing bearings, IP-rated controls, and protective covers.
By Material Type
- Glass & Panels: Vacuum glass lifters reduce fingerprints, edge chips, and breakage while improving placement accuracy.
- Stone, Blocks, and Slabs: Purpose-built block lifting clamps stabilize the load and protect finish.
- Sheet Metal & Components: Magnets or grippers with quick-change interfaces keep takt time tight.
By Workflow & Ergonomics
- Remote Controls enhance line-of-sight safety and keep operators out of pinch points.
- Low-Headroom Trolleys/Hoists increase lift height in retrofit spaces.
- Rotation Limits avoid collisions with walls, racking, and conveyors.
Specifying Key Jib Crane Components: A Practical Checklist
Use this punchy list when writing your RFQ or comparing quotes:
- Capacity & Duty
- Rated capacity with 15–20% buffer above typical peak load
- Hoist duty class aligned to cycles/hour and shift count
- Coverage & Geometry
- Reach, under-boom clearance, hook path, and swing arc
- Obstruction map (columns, mezzanines, doors)
- Slewing & Positioning
- Manual vs. powered slewing; startup torque and braking
- Rotation limits, mechanical stops, and anti-collision
- Trolley & Hoist
- Speeds (single, dual, VFD), soft start/stop
- Low-headroom options; shock load mitigation
- End Effectors
- Match to material: glass lifter or block lifting clamp
- Quick-change couplers if multiple load types
- Controls & Power
- Pendant vs. radio; channel management and interference testing
- Festoon, energy chain, or slip ring for powered slewing
- Safety & Compliance
- Overload limits, upper/lower stops, e-stops, torque limiter
- Documentation for inspections and logbooks
- Installation & Structure
- Base plate, anchors, grout plan (for column jibs)
- Wall steel verification (for wall-mounted)
- Serviceability
- Grease points, access panels, parts availability
- Maintenance intervals and recommended spares kit
Maintenance: Keeping Jib Crane Components in Peak Condition
Even perfectly specified jib crane components degrade without care. A simple program pays off:
- Daily/Weekly: Visual checks on hooks, slings, latches; listen for bearing noise; confirm limit switch operation.
- Monthly/Quarterly: Inspect trolley wheels and track wear; verify hoist chain/rope condition and lubrication; torque-check fasteners; test brakes.
- Annually: Formal inspection with load test; slew bearing backlash measurement; electrical insulation testing; control calibration.
Unsure whether to fix or swap? Read: When Should Jib Crane Components Be Replaced or Repaired?
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Underspec’d Hoist Duty Class
Choosing “good enough” for a busy line leads to overheating and premature motor failures. - Ignoring Foundation Requirements
Column jibs demand proper anchor design and floor thickness; shortcuts risk base plate movement and misalignment. - Mismatched End Effectors
Using generic hooks for delicate materials like glass or polished stone increases scrap and injury risk. Adopt dedicated glass lifter or block lifting solutions. - No Rotation Limits
Full 360° swing in tight bays can cause collisions. Fit hard stops or programmable limits. - Skipping Cable Management
Poor festoon or energy chain design leads to snagging and downtime.
When an Articulated Jib Makes the Difference
Articulated designs add a “elbow” to the boom, allowing the outer arm to move independently. This:
- Navigates around pillars and machinery
- Keeps loads closer to the operator’s natural reach zone
- Reduces re-positioning and improves placement accuracy
If floor space is at a premium or your workflow is cell-based, consider the Articulated Jib Crane – Wall Mounted as a compact, agile alternative.
FAQs About Jib Crane Components
How do I size the hoist and trolley correctly?
Start with true peak load (include rigging), then choose a hoist duty rating for your cycles per hour and daily runtime. Trolley wheel material and flange geometry should match boom profile and environment to reduce track wear.
What influences slewing smoothness?
Bearing type, lubrication regime, and startup torque are key. Powered slewing with VFD provides soft acceleration, reducing load swing and improving placement precision.
Do I need specialized lifting attachments?
If you handle sensitive or irregular materials, yes. Vacuum glass lifters or purpose-built block lifting clamps dramatically cut damage and improve grip security compared to generic hooks.
How often should I inspect jib crane components?
Perform operator checks daily/weekly and schedule formal inspections at least annually (or per local standards). Critical parts—hoist brakes, limit switches, slewing bearings—warrant extra attention.
The Bottom Line: Components Drive Outcomes
The smartest path to safer lifts, faster cycles, and lower lifetime cost is to optimize your jib crane components—not just the crane type. Map the work envelope, duty profile, and materials, then select a hoist/trolley combo, slewing solution, and end effector that fit the job, not the other way around.
When you’re ready to explore configurations and compare options, browse more crane products, including compact articulated models and application-specific lifters like the glass lifter and block lifting solutions.
Quick Buyer’s Recap
- Size capacity with a safety buffer and match duty class to cycles.
- Confirm reach, clearance, and swing arc against your obstruction map.
- Choose end effectors that fit the load—they’re the make-or-break link.
- Engineer the base or wall fixings properly; don’t shortcut anchors.
- Plan maintenance access and stock critical spares from day one.
With the right jib crane components, your lifting system becomes a productivity asset—not a maintenance liability.















Please log in to leave a comment.