Safe handling and disposal of hazardous waste is a crucial aspect of material handling, particularly in industries like construction, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and logistics. Mishandling such materials can lead to serious health hazards, environmental damage, and costly regulatory penalties.
In this article, we explore effective methods for handling hazardous materials, the importance of material handling equipment, and compliance strategies that businesses must adopt. Whether you’re dealing with corrosives, flammables, toxic chemicals, or biohazardous waste, the goal is the same: minimize risk, ensure worker safety, and comply with national and international safety standards.
🔗 What Is the Basis for the Storage of Classified Material Handling?

Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Hazardous Material and Waste
What Is Hazardous Waste?
Hazardous waste refers to materials that pose a significant threat to human health or the environment due to their chemical, biological, or radiological properties. These may include:
- Flammable liquids and gases
- Toxic chemicals
- Infectious biological waste
- Reactive or explosive substances
- Heavy metals and solvents

Methods for the Safe Handling of Hazardous Waste
1. Segregation at the Source
One of the most effective methods for safe material handling is segregating hazardous materials at the point of origin. Materials should be classified based on:
- Reactivity
- Toxicity
- Flammability
- Corrosiveness
Proper segregation prevents dangerous chemical reactions, contamination, or fire hazards and is a critical part of industrial material handling solutions.
2. Using Appropriate Material Handling Equipment
Using the right material handling equipment is vital when working with hazardous substances. Key tools include:
- Vacuum Lifters for enclosed, touchless lifting
🔗 View Vacuum Lifters - Paver Lifters for outdoor, hazardous environments
🔗 Vacuum Paver Lifter AVPL40 - Aardwolf Slab Lifters for heavy-duty, flat materials
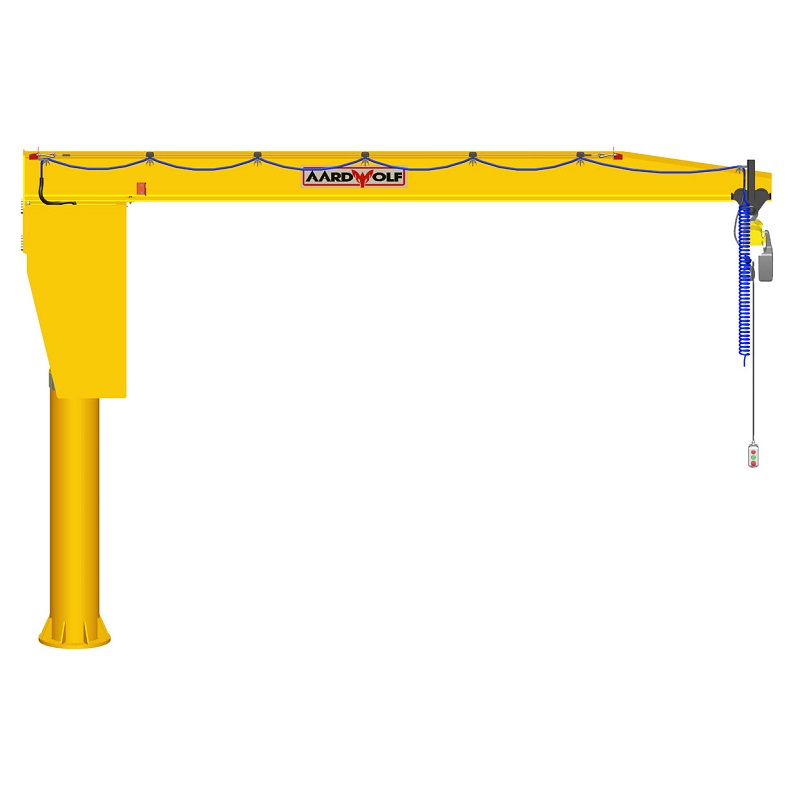
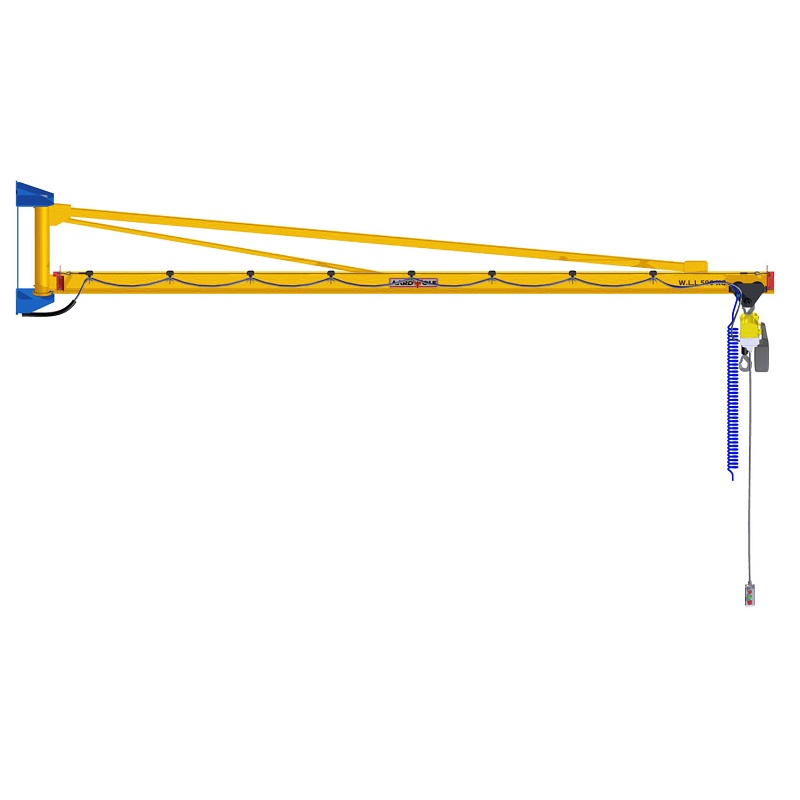
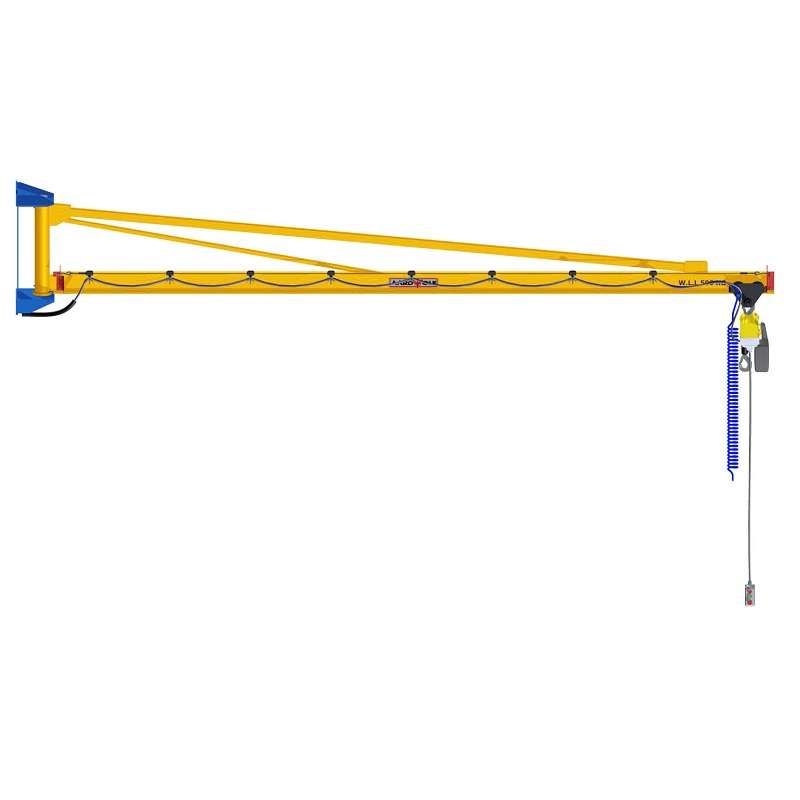
🔗 Aardwolf Slab Lifters - Jib Cranes to enable secure, elevated material movement
🔗 Jib Cranes
These tools reduce human exposure and are especially effective in pharmaceutical material handling systems and material handling in construction.
3. Utilizing Containment Systems
Bulk material handling systems and specialized containment units are essential to store hazardous materials securely. These should include:
- Double-walled drums or IBCs
- Spill pallets and secondary containment trays
- Flame-resistant cabinets
- Explosion-proof lockers for flammable gases
Pairing these with warehouse material handling equipment enhances operational safety.
4. Labeling and Documentation
Proper labeling in accordance with GHS (Globally Harmonized System) and maintaining Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) is non-negotiable.
Each container should include:
- Chemical identity
- Hazard symbols
- Handling instructions
- Emergency response steps
This is integral to maintaining material handling safety standards.
5. Automated Material Handling Systems
Where risk levels are high, automated material handling systems reduce human interaction. These systems can include:
- Conveyor belts with leak sensors
- Robotic arms for reactive material handling
- Smart storage systems with environmental monitoring
These solutions ensure precision and compliance in material handling in logistics and material handling for manufacturing environments.
Disposal Best Practices for Hazardous Waste
1. Neutralization or Treatment
Before disposal, some hazardous materials can be neutralized or treated to reduce their hazardous nature—commonly used in material handling for food industry and pharmaceuticals.
2. Secure Transport Using Certified Equipment
Transporting hazardous waste must involve:
- Sealed manual material handling tools
- Tracked shipping containers
- GPS-monitored fleets
- Compliance with DOT and EPA transport laws
Using forklifts for material handling with secured containment units ensures safer movement.
3. Partnership with Certified Disposal Vendors
Companies must collaborate with licensed waste management firms to ensure compliance and secure disposal. Always vet your material handling system suppliers and disposal partners.
Employee Safety: A Top Priority
1. Training and Certification
All employees handling hazardous materials must undergo:
- Material handling training programs
- Emergency response drills
- Refresher courses on updated regulations
🔗 How Does Material Handling Impact the Human Labor Force?
2. PPE and Dress Code Compliance
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential. This includes:
- Chemical-resistant gloves and suits
- Full-face respirators
- Heat-resistant footwear
- Eye protection and hearing protection
🔗 Loose Clothing Is Best to Wear When Handling Material?
3. Emergency Planning
Facilities should have:
- Spill kits
- Eye wash stations
- Fire extinguishers rated for chemical fires
- Isolation areas
Smart Design: Building a Safer Handling System
Design Considerations
- Automated vs Manual Material Handling balance
- Flow-through layout for hazardous areas
- Proximity of exits and safety equipment
- Remote monitoring of containment systems
🔗 What Is Material Handling? Types, Equipment, Functions, Safety, and Warehouse Optimization
Final Thoughts
Hazardous material and waste handling isn’t just a regulatory formality—it’s a cornerstone of workplace safety and environmental responsibility. By combining the right tools, training, procedures, and partners, businesses can build heavy-duty material handling solutions that keep people and the planet safe.
Want to improve your safety protocols or upgrade to the best material handling equipment for warehouses? Explore options from Aardwolf today:














Please log in to leave a comment.