In modern workshops, warehouses, and small production lines, every square meter counts. Managing space effectively while handling heavy materials can be challenging — especially when large cranes or forklifts aren’t an option. This is where jib crane components designed for compact work environments provide an efficient, flexible, and safe solution.
This article explores the different types of jib crane components that are ideal for space‑limited areas, their working principles, and practical ways to optimize lifting operations in small workshops or industrial setups.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction: The Need for Compact Jib Crane Components
Tight spaces — like assembly lines, garages, and stone fabrication shops — require precise load handling equipment that doesn’t occupy much floor area. Unlike overhead or gantry cranes, jib cranes can be mounted on walls, columns, or small pedestals, making them an excellent choice for limited work zones.
Compact jib crane systems are engineered with efficient mechanical and electrical components that ensure:
- Maximum reach within confined areas
- Smooth rotation and lifting movement
- Low‑maintenance operation
- Enhanced safety for operators
Their modular design means the system can be installed, relocated, or upgraded with minimal downtime.
Explore how components enhance crane performance: How Do Jib Crane Components Improve Load Handling?
2. Understanding the Core Jib Crane Components
A jib crane’s efficiency depends on how well each component works in tandem. Let’s look at the essential elements that make up these versatile cranes.
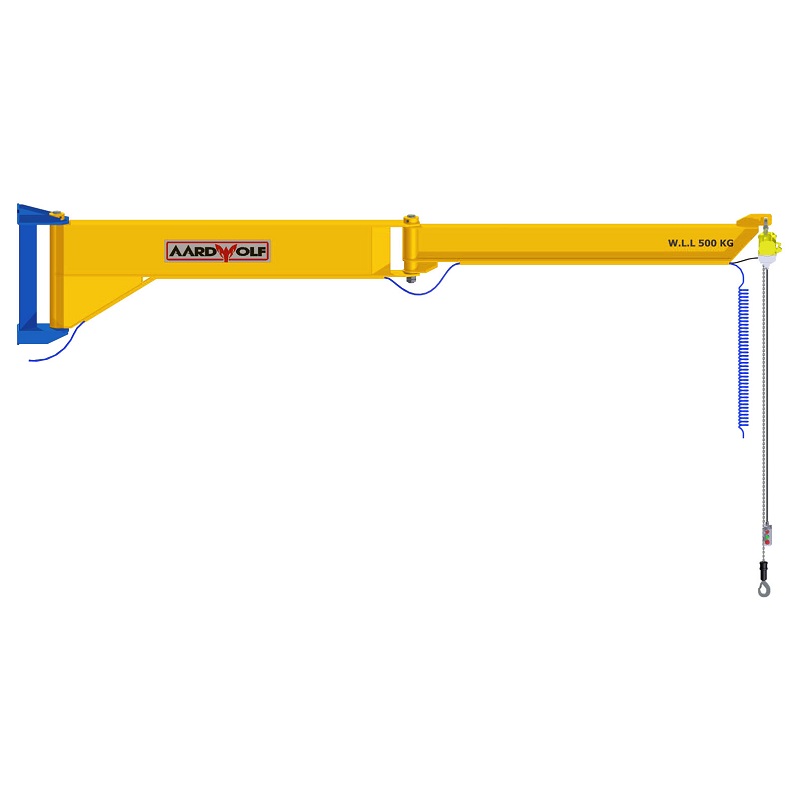
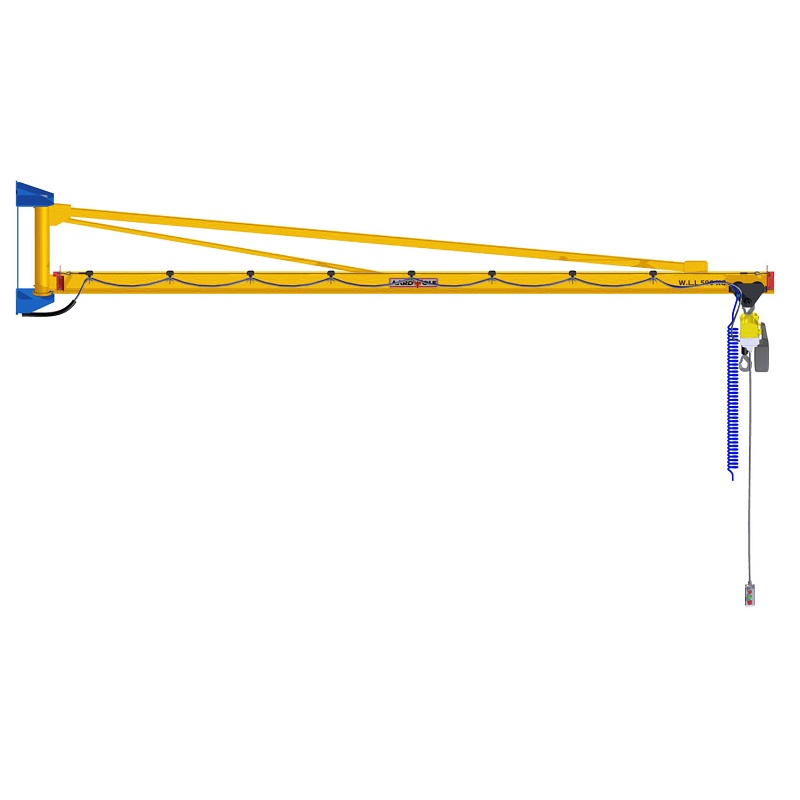
a. The Boom (Jib Arm)
The boom is the horizontal arm responsible for carrying and moving the load. For small spaces, booms are often shorter (2–5 meters) and constructed using I‑beams or box girders to maintain strength while minimizing footprint.
- Low‑profile booms allow smooth operation under low ceilings.
- Box girder designs help prevent deflection in tight conditions.
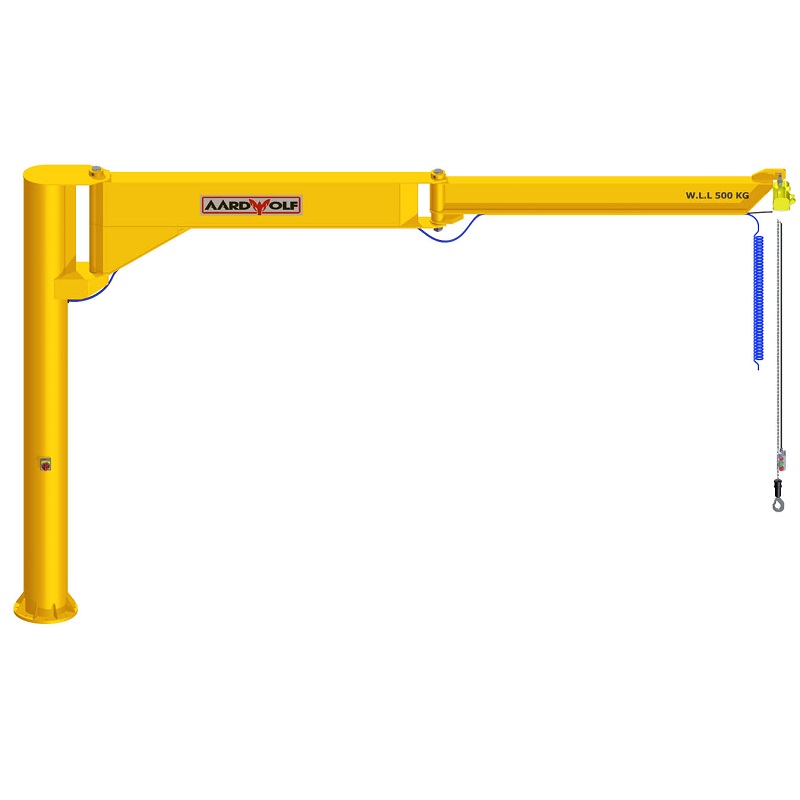
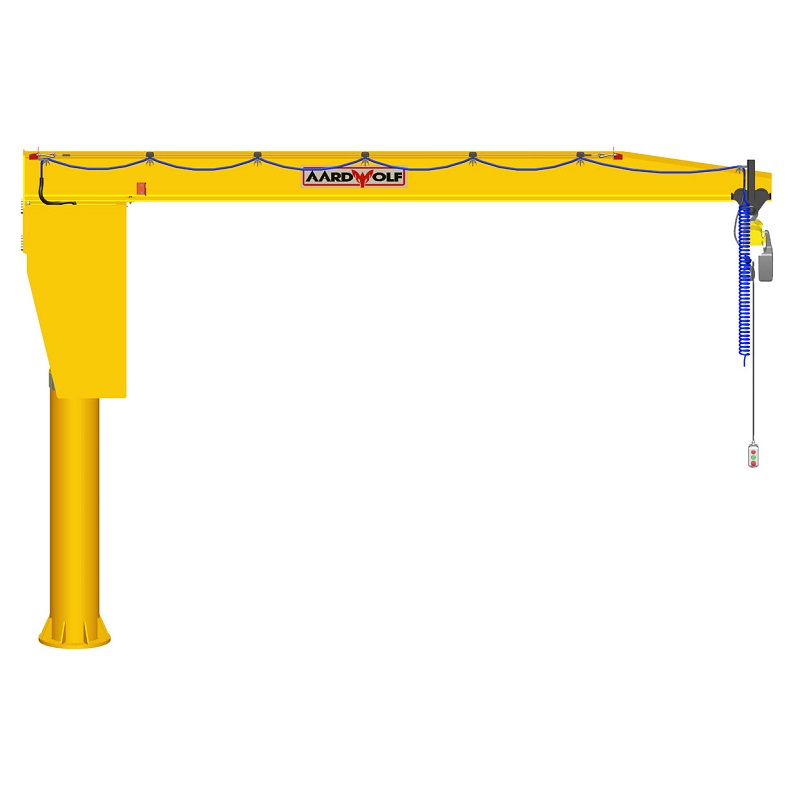
b. The Mast or Column
The mast serves as the vertical support structure for freestanding cranes. In small environments, lightweight steel tubular masts are preferred.
- Wall‑mounted cranes eliminate the mast entirely — a big advantage in workshops with minimal floor space.
- For added versatility, consider Articulated Jib Crane – Wall Mounted designs that rotate easily in tight areas. Learn more about this compact design: Articulated Jib Crane – Wall Mounted
c. The Hoist and Trolley
The hoist lifts the load, while the trolley allows horizontal movement along the boom.
For small‑space applications:
- Choose electric chain hoists for lighter loads (250–2000 kg).
- Opt for low‑headroom hoists where ceiling height is limited.
- Select compact trolleys with smooth bearings for quiet operation.
d. Rotation Mechanism
Rotation is essential for maneuverability. Depending on the installation type, manual or motorized slewing systems are used.
- 180° rotation suits wall‑mounted cranes.
- 360° rotation applies to freestanding designs.
Compact bearings and slewing rings reduce turning resistance and ensure steady operation.
e. Base and Mounting System
Mounting systems vary by space type:
- Wall‑mounted bases are ideal for narrow workshops.
- Foundation‑less pedestal mounts work for portable or rental sites.
- Reinforced bolt‑down bases offer stability for concrete floors.
3. Specialized Components Designed for Small Work Areas
Not all jib crane setups are identical. Certain component variations are purpose‑built to fit confined spaces without compromising performance.
1. Low‑Headroom Hoists
Compact hoists minimize the distance between the hook and the boom, allowing for greater lifting height under low ceilings — crucial for basement workshops or container facilities.
2. Articulated Booms
These two‑part booms bend or pivot midway, making them perfect for lifting around corners or inside small bays.
They’re particularly valuable in stone fabricator environments where materials must move precisely between cutting and polishing stations.
See related topic: Stone Fabricator
3. Motorized Slewing Units
Compact motorized slewing kits allow smooth 180°–360° rotation in restricted areas.
These are often used with light‑duty jib cranes installed on production floors where precision load placement is critical.
4. Portable Bases and Mobile Units
Some jib crane components are modular and mobile, allowing the crane to move across workstations. Combined with a material handling trolley, this provides unmatched flexibility for multipurpose environments.
Learn more: Material Handling Trolley
4. How Compact Jib Crane Components Solve Space Challenges
Efficient use of jib crane components directly improves workflow in tight areas.
| Challenge | Component Solution | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Limited floor area | Wall‑mounted or column‑mounted bases | Saves valuable workspace |
| Low ceilings | Low‑headroom hoists | Maximizes lifting height |
| Tight corners | Articulated booms | Enables multi‑angle lifting |
| Restricted movement | Motorized slewing mechanisms | Smooth rotation and control |
| Frequent layout changes | Portable base systems | Rapid repositioning |
These systems reduce manual handling by up to 30%, improving productivity while minimizing strain on workers.
Deep dive: What Makes Jib Crane Components Different from Others?
5. Maintenance Considerations for Compact Jib Cranes
Even in small environments, regular maintenance ensures longevity and performance.
Key actions include:
- Lubricating trolley bearings and rotation mechanisms monthly.
- Inspecting hoist chains for wear or elongation.
- Checking anchor bolts on wall mounts.
- Repainting exposed steel to prevent corrosion.
For more details on inspection intervals, read: Which Jib Crane Components Need Regular Maintenance?
6. Applications of Compact Jib Crane Systems
Compact jib cranes are widely used in:
- Automotive workshops for component handling
- Stone fabrication plants for slab movement
- Warehouses with narrow aisles
- Assembly lines in electronics and machine manufacturing
- Small construction projects where overhead cranes aren’t feasible
In these setups, component flexibility enables efficient lifting even under height and width restrictions.
7. Selecting the Right Jib Crane Components
When choosing components for space‑limited work zones, consider:
- Load capacity (typically 150 kg–2000 kg for small cranes)
- Available height and ceiling clearance
- Rotation range (180° or 360°)
- Mounting type (wall, floor, or column)
- Duty cycle based on daily use
- Power supply type (manual, electric, or pneumatic)
Consulting with specialists helps ensure compliance with ISO, FEM, and CMAA standards while tailoring the crane to your workspace layout.
8. Conclusion
Compact jib crane components are engineered for precision, safety, and adaptability — making them indispensable in space‑restricted industrial environments. From articulated booms to low‑headroom hoists, each component serves a specific purpose that enhances lifting efficiency while conserving floor area.
By selecting the right configuration and maintaining it properly, businesses can achieve 20–30% higher productivity in confined work areas.
For professional‑grade lifting solutions and component configurations, visit
👉 More Crane Products













Please log in to leave a comment.