In industrial environments where efficiency and safety intersect, jib crane components play a vital role in keeping lifting operations both productive and secure. From workshops and warehouses to stone fabrication sites and construction yards, these systems handle the demanding task of lifting and moving heavy materials safely.
However, even the most durable cranes rely on consistent safety inspections and component checks to maintain reliability. A single overlooked part—whether a bearing, chain, or mounting bolt—can compromise the system’s integrity.
In this article, we explore how jib crane components contribute to workplace safety, what to check during routine inspections, and how to establish a proactive maintenance strategy to minimize risks and downtime.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Why Safety Checks for Jib Crane Components Matter
Every workplace aims to protect its people and assets. Jib cranes, while compact and efficient, operate under heavy loads and repetitive cycles. Without regular component inspections, even minor wear can lead to:
- Equipment failure or tipping due to loose bolts or damaged bearings
- Load slippage from worn hooks or hoist chains
- Operator injury caused by poor mechanical control or electrical faults
Performing structured safety checks ensures compliance with OSHA and ISO standards, extending the crane’s lifespan while preventing costly downtime.
👉 Learn how these systems drive productivity:
How Can Jib Crane Components Enhance Productivity?
2. Key Jib Crane Components Involved in Safety Inspections
Each component in a jib crane works together to provide balance, stability, and control. During a safety check, technicians must assess the following parts to verify proper operation and detect early signs of wear.
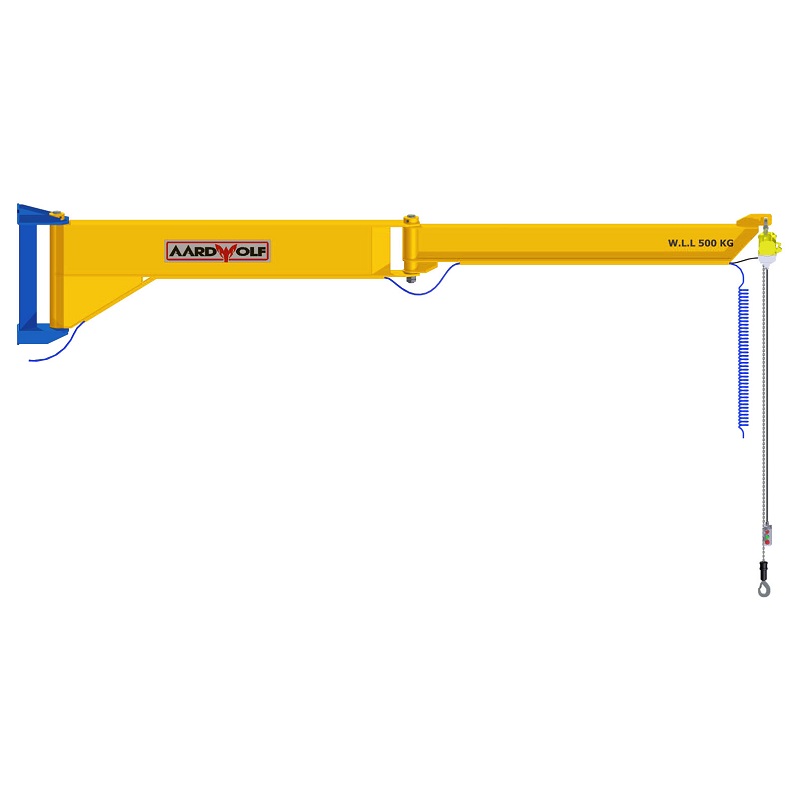
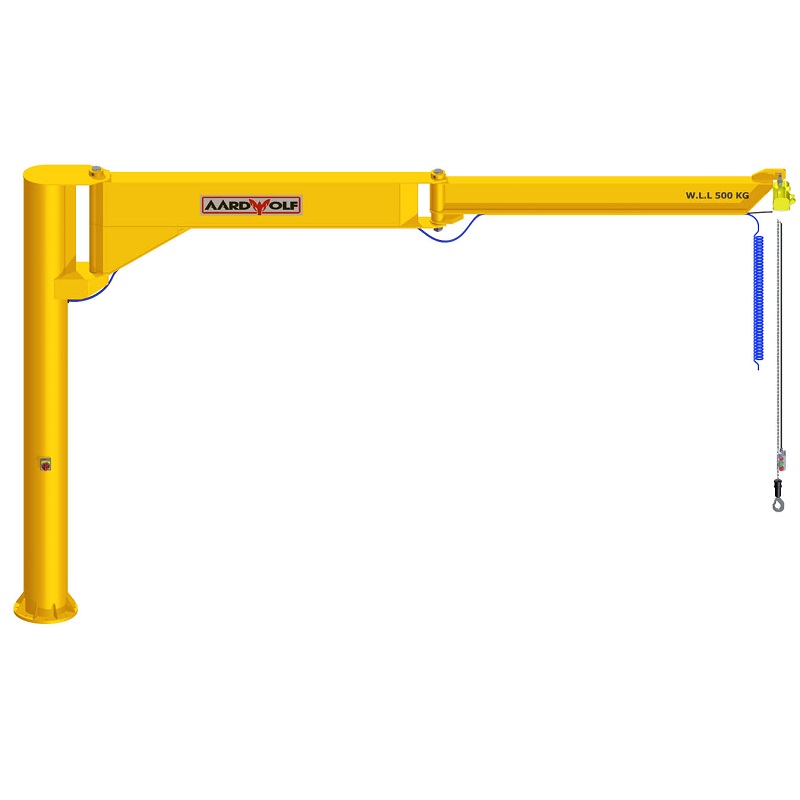
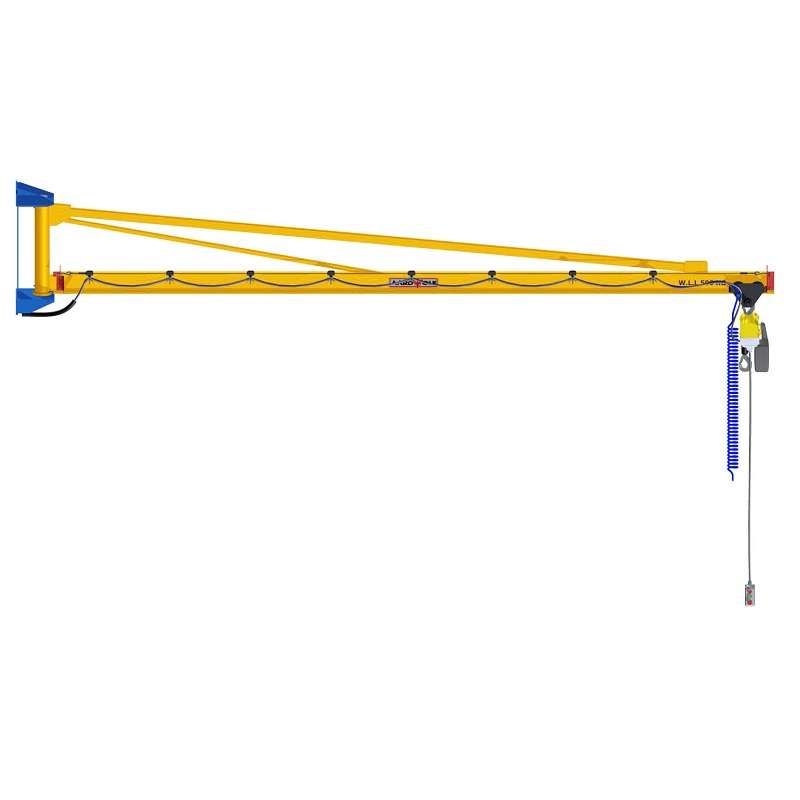
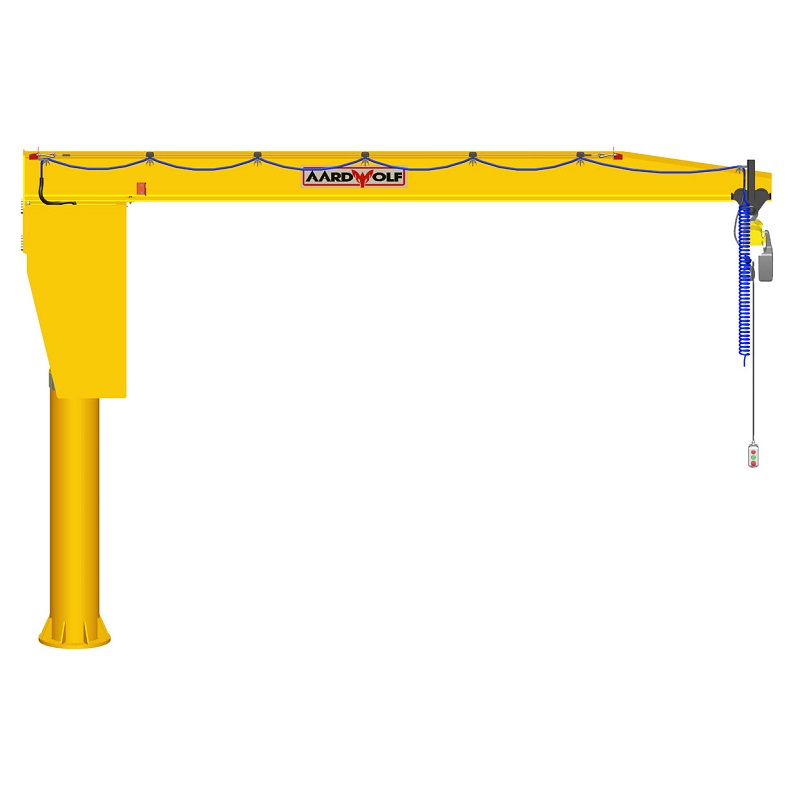
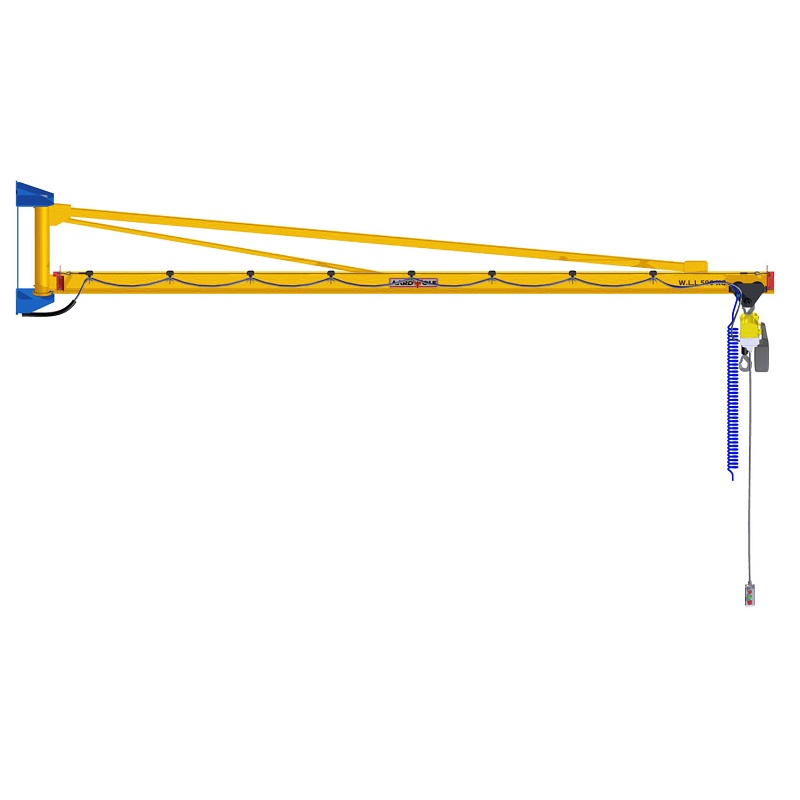
a. The Jib Arm (Boom)
The boom supports horizontal movement and load bearing. Inspect for:
- Structural cracks or metal fatigue
- Rust, corrosion, or surface dents
- Proper alignment and rotation clearance
A compromised boom reduces the crane’s load capacity, creating imbalance during lifting.
For confined work areas, compact boom structures improve safety and ergonomics. Learn more:
What Types of Jib Crane Components Fit Small Spaces?
b. The Mast or Column
The mast provides vertical stability. Check for:
- Anchor bolt integrity and floor plate cracks
- Base corrosion or bending
- Any signs of concrete foundation wear
Wall-mounted systems, such as the Articulated Jib Crane – Wall Mounted, should also be inspected for bracket tightness and weld quality.
c. Hoist and Trolley System
The hoist performs the lifting, while the trolley allows side movement. Regular inspections should include:
- Wire rope or chain wear, kinks, or elongation
- Brake efficiency and stopping distance
- Lubrication of trolley wheels and bearings
A malfunctioning hoist can lead to uncontrolled load descent or jerky movement—both high-risk scenarios in stone fabrication facilities or warehouses.
Learn more about maintaining these assemblies:
When Should Jib Crane Components Be Replaced or Repaired?
d. Rotation and Slewing Mechanisms
Smooth rotation ensures stable and predictable movement. Check for:
- Bearing friction or excessive play
- Gear noise or grinding
- Proper lubrication and electrical control
Uneven slewing movement can cause load sway, particularly dangerous when working near equipment, vehicles, or stacked materials.
e. Electrical Controls and Limit Switches
Electrical systems keep crane motion predictable and prevent overloads. Inspect for:
- Proper functioning of limit switches
- Clean contactors and corrosion-free connections
- Intact insulation on power cables
If electrical controls are inconsistent or unresponsive, the entire crane becomes unsafe to operate. Regular calibration ensures accuracy and response reliability.
3. How Safety Checks Prevent Common Jib Crane Hazards
Consistent monitoring of jib crane components helps identify issues before they escalate into operational hazards. Let’s look at key areas where preventive checks reduce risks:
| Potential Hazard | Component to Inspect | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Load swing or drop | Hoist chain, trolley, hooks | Check for wear and lubricate moving parts |
| Structural failure | Boom, mast, bolts | Tighten anchor points and inspect welds |
| Electrical malfunction | Control panel, cables | Test voltage and inspect insulation |
| Operator strain | Controls, rotation bearings | Maintain smooth movement and ergonomics |
4. Safety Inspection Frequency and Compliance
Safety checks should follow structured inspection intervals, based on usage intensity:
| Usage Type | Frequent Inspection | Periodic Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Light duty (occasional lifting) | Monthly | Annual |
| Moderate duty (daily use) | Weekly | Semi-annual |
| Heavy duty (continuous or outdoor) | Daily | Quarterly |
Frequent inspections cover visual and functional checks by operators, while periodic inspections are performed by certified professionals.
For outdoor or corrosive environments, consider protective coatings and regular cleaning—especially around kerb stone or concrete dust work zones.
Related: Kerb Stones
5. Common Findings During Safety Audits
Routine audits often reveal early-stage component issues that can be resolved before causing system failure:
- Loose fasteners from vibration or misalignment
- Worn chain guides or rollers leading to uneven movement
- Overheated motors from continuous operation without rest
- Cracked welds on mounting brackets
- Overloaded hoists from miscalculated lifting limits
Regular maintenance ensures each part performs as intended, maintaining both operator confidence and workplace safety.
6. Documenting and Acting on Inspection Results
Safety checks are only effective if findings are documented and addressed promptly. Create an inspection log including:
- Component condition ratings (e.g., good, worn, critical)
- Maintenance actions taken
- Next inspection schedule
- Technician signatures and certifications
Digital maintenance tracking systems or QR-based checklists make compliance easier and ensure accountability.
7. Integrating Safety Checks with Productivity Goals
Many assume frequent inspections slow down workflow. In reality, maintaining your jib crane system enhances productivity by minimizing breakdowns, preventing injuries, and improving load precision.
Safety-driven efficiency aligns with modern lean manufacturing principles—optimizing uptime, reducing waste, and ensuring consistent performance.
For more insights: How Can Jib Crane Components Enhance Productivity?
8. Training: The Human Component of Crane Safety
Even the best-maintained crane can be dangerous without skilled operators. Training should focus on:
- Pre-operation visual checks
- Load rating awareness
- Emergency stop usage
- Recognizing unusual noises or motion irregularities
Operators should report concerns immediately, allowing technicians to isolate and address issues early. Safety is a shared responsibility between the team and the machinery.
9. The Role of Preventive Maintenance in Long-Term Safety
Incorporating preventive maintenance schedules ensures cranes remain reliable. Regular component replacements—such as hoist chains, bearings, and cables—extend the crane’s lifecycle and reduce unplanned downtime.
Facilities engaged in heavy stone fabrication or high-dust environments should adopt shorter maintenance cycles to counteract abrasive particles affecting bearings and joints.
Discover more: Stone Fabrication
10. Conclusion
Every jib crane component—from the smallest bolt to the main boom—plays an essential role in safety. Routine inspections, timely replacements, and trained operators together create a resilient system that protects workers, equipment, and productivity.
Incorporating structured safety checks into your maintenance plan ensures consistent operation and regulatory compliance, reinforcing both efficiency and trust in your workplace.
For reliable, high-quality crane systems and replacement components, explore:
👉 More Crane Products














Please log in to leave a comment.