Material handling is the lifeline of industries such as construction, manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics. Without the right equipment, even the most skilled workforce can face delays, higher costs, and safety risks. Whether you’re managing a job site or running a busy warehouse, understanding the types of material handling equipment is crucial to maximizing efficiency, reducing labor costs, and keeping your workplace safe.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the major categories of material handling equipment, their specific uses, and how they help your operation thrive.
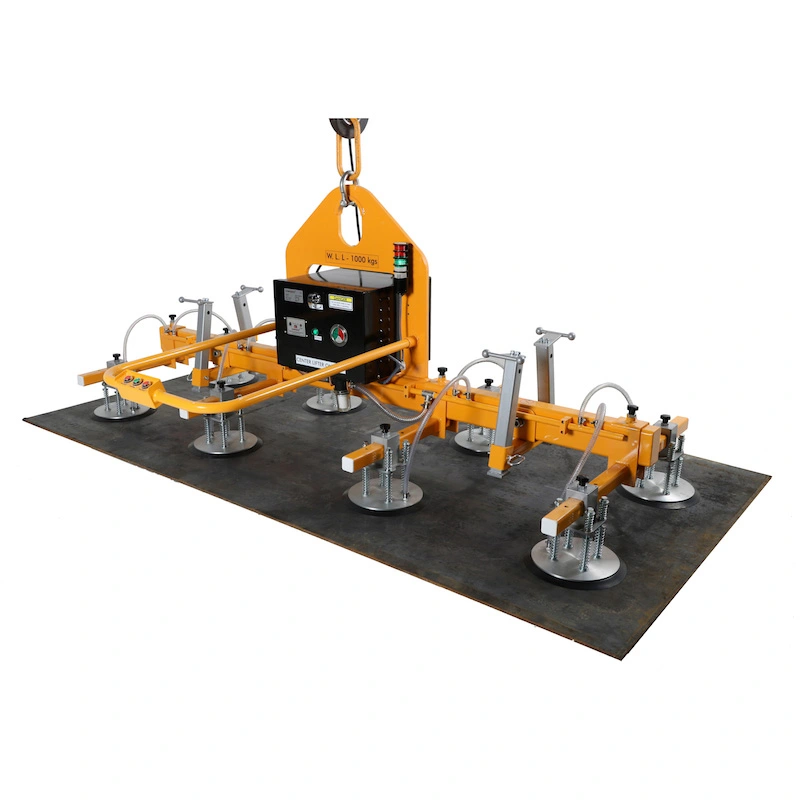

Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Material Handling?
Material handling involves the movement, protection, storage, and control of materials throughout manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, and construction. The right equipment and strategies ensure materials flow seamlessly from one point to another, optimizing productivity and minimizing waste.
For an in-depth overview, visit What Is Material Handling?
Why Is Material Handling Equipment Important?
- Reduce labor cost in construction and warehousing
- Improve safety on construction site
- Increase construction and operational productivity
- Minimize material waste
- Ensure effective material storage solutions
- Streamline transporting materials on job sites
- Support efficient construction site logistics
1. Transport Equipment
This category moves materials from one location to another, either within a facility or across a construction site.
- Forklifts for construction: Powered vehicles used to lift and move heavy loads, pallets, and materials over short distances.
- Pallet jacks and carts: Simple yet vital for quickly moving loads inside warehouses and distribution centers.
- Wheelbarrows and dollies: Essential for small-scale moving and maneuvering in tight spaces.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs): Robots designed to move materials without human intervention.
- Conveyors in construction: Mechanized systems that continuously transport bulk materials or packages.
Explore more in Material handling Equipment and Material-handling Equipment.
2. Storage and Handling Equipment
These systems are designed for holding materials for periods of time.
- Pallet racks and shelving: Organize goods vertically, maximizing warehouse space.
- Bins, drawers, and containers: Protect materials and make small items easy to retrieve.
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS): Computer-controlled systems for high-density storage and fast picking.
A good material storage solution prevents clutter, damage, and lost inventory.
3. Unit Load Formation Equipment
This category creates unit loads that are easier and safer to move.
- Pallets and skids: Flat structures that support goods for lifting by forklifts or pallet jacks.
- Containers and crates: Secure loose items and protect them during handling.
- Aardwolf Slab Lifters: Aardwolf Slab Lifters safely lift, move, and position heavy stone, glass, or metal slabs on job sites.
4. Lifting and Positioning Equipment
This equipment raises, lowers, or positions materials for assembly, storage, or movement.
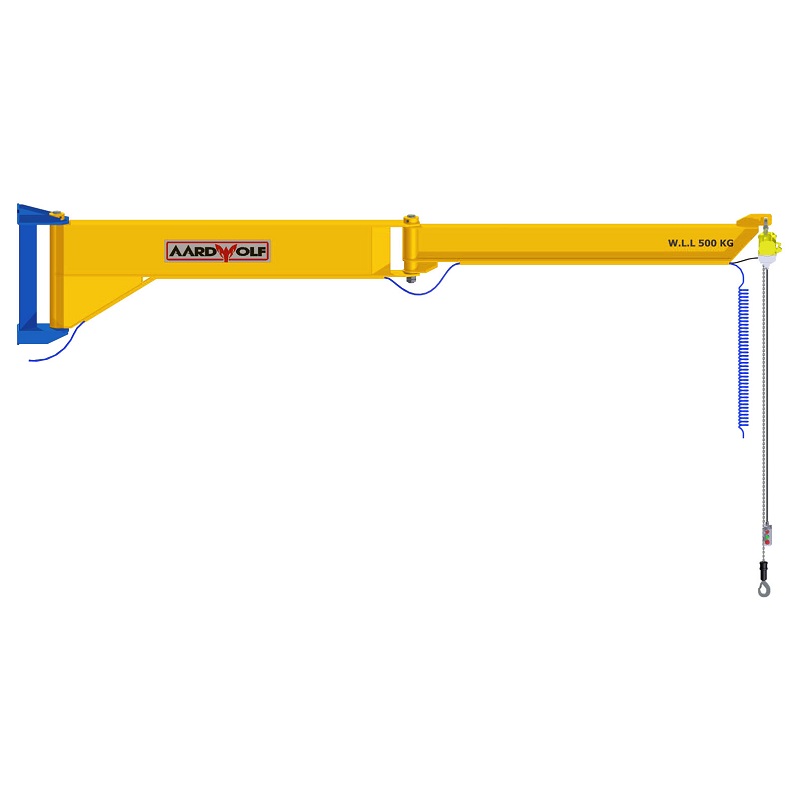
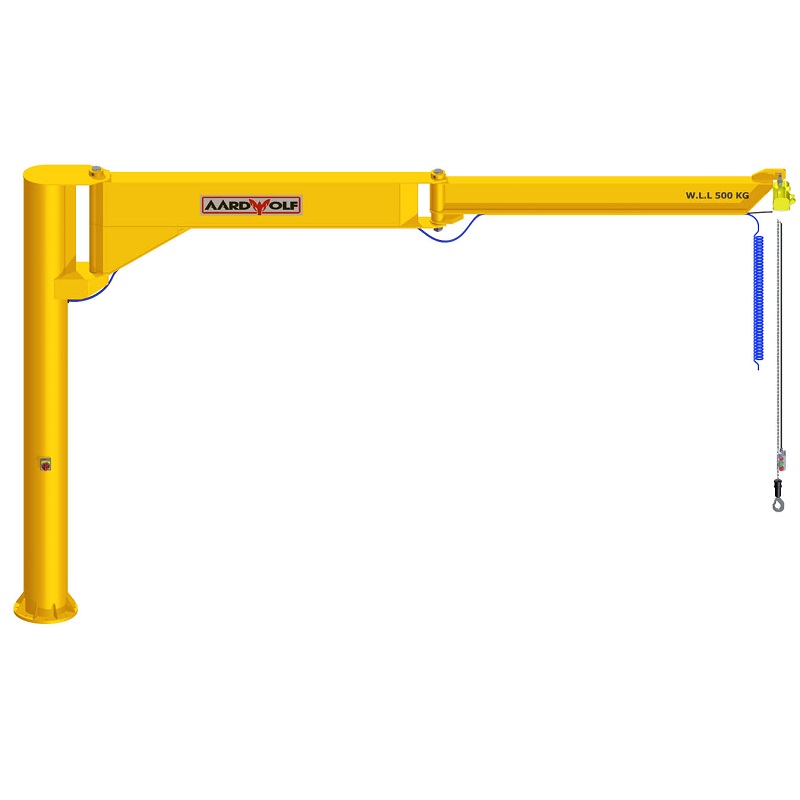
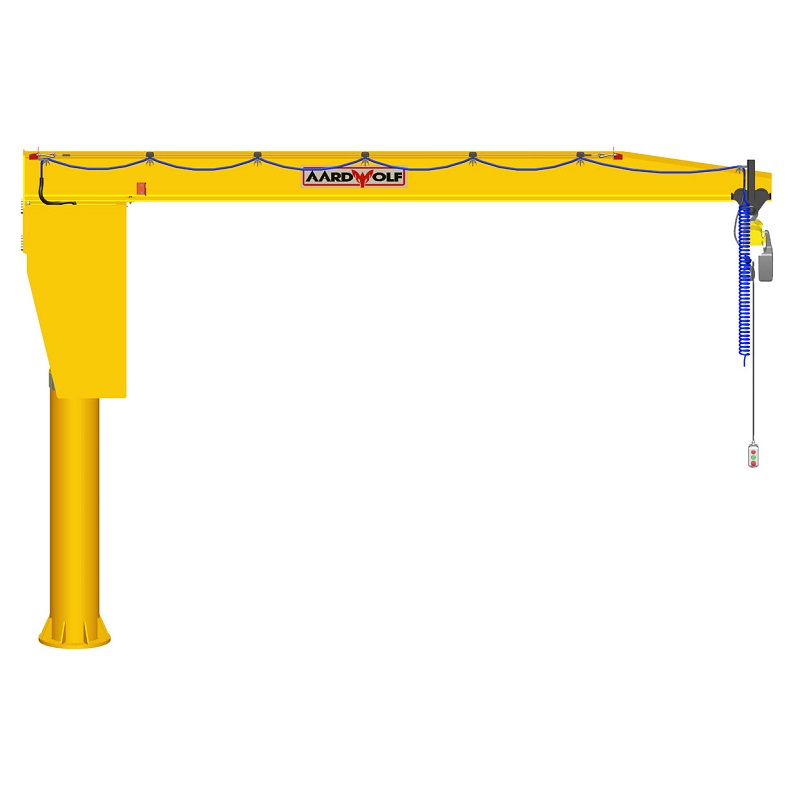
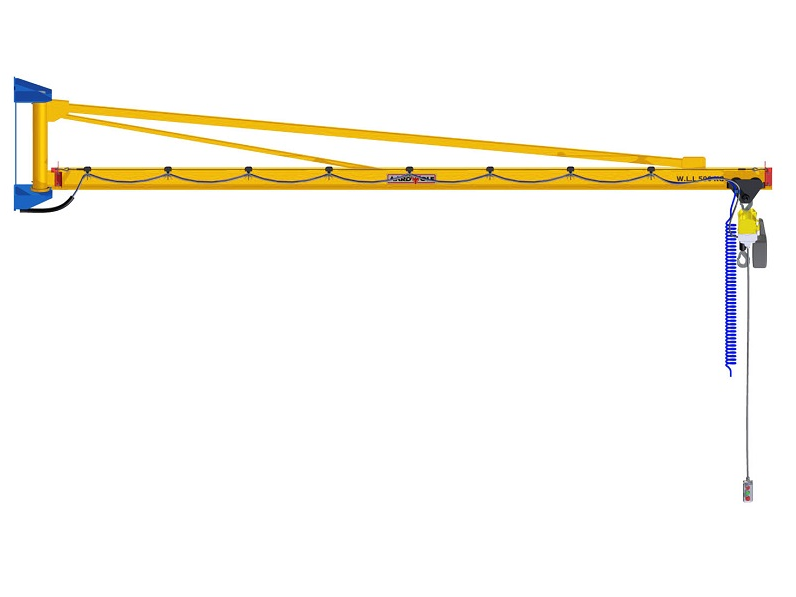
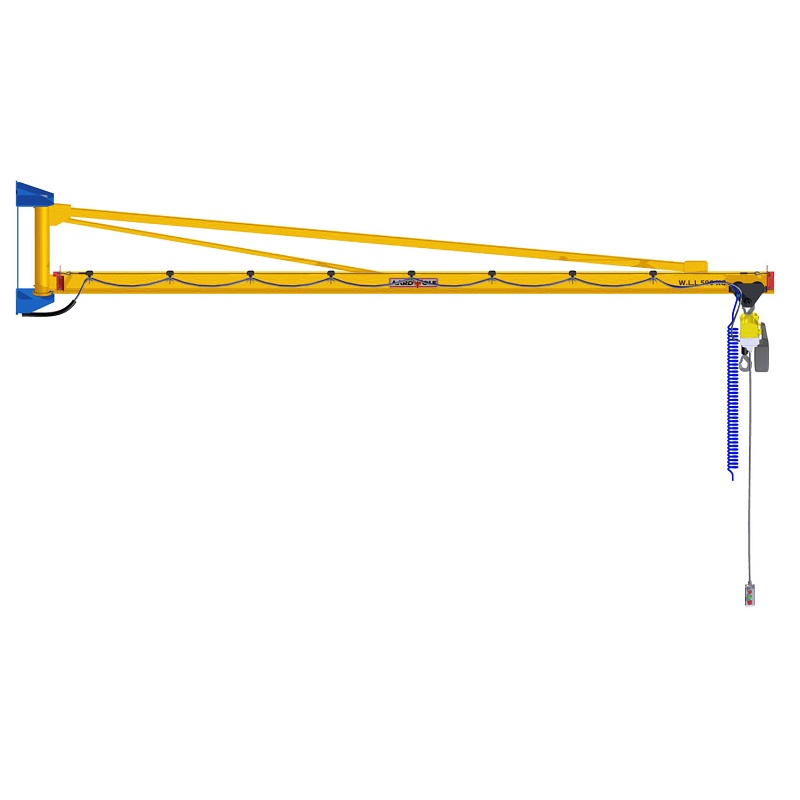
- Hoists and cranes: Jib Cranes, gantry cranes, and tower cranes lift heavy loads safely to higher or distant locations.
- Vacuum Lifters: Vacuum Lifters use suction power to handle delicate or heavy panels, reducing manual labor and minimizing breakage.
- Scissor lifts and lift tables: Elevate goods or workers to required heights in a controlled manner.
5. Bulk Material Handling Equipment
Used for moving, storing, and controlling loose bulk materials.
- Conveyors in construction: Move sand, gravel, or grain automatically to where they are needed.
- Hoppers and silos: Store and dispense bulk materials in a controlled flow.
Manual, Motorized, and Automated Equipment: What’s the Difference?
- Manual: Simple tools like hand trucks, dollies, and wheelbarrows. Suitable for light loads and flexible use but can be labor-intensive.
- Motorized: Powered equipment such as forklifts for construction and electric pallet jacks. Faster, safer, and ideal for heavier materials.
- Automated: High-tech solutions like AGVs, robotic arms, and automated storage that minimize labor, increase speed, and improve inventory accuracy.
Learn about these differences at What Is Material Handling Equipment?.
Selecting the Right Equipment: Key Considerations
- Material type, size, and weight
- Volume and frequency of movement
- Space and layout constraints
- Safety and compliance standards
- Budget and ROI
For detailed selection strategies, see Material-handling Equipment.
Benefits of Using the Right Material Handling Equipment
- Reduces risk of injury and accidents
- Optimizes workflow and reduces bottlenecks
- Improves order accuracy and customer satisfaction
- Protects inventory and reduces product loss
- Supports lean and just-in-time (JIT) strategies
Real-World Example
A construction company adopted Aardwolf Slab Lifters, Vacuum Lifters, and Jib Cranes to handle heavy panels and slabs. This led to a 40% reduction in labor costs, a 30% improvement in site safety, and faster project completion.
Conclusion
Material handling equipment comes in many forms, each suited for specific materials, tasks, and environments. From simple carts to automated cranes and lifters, these tools are vital for efficient, safe, and cost-effective operations in construction, warehousing, and logistics.
To explore solutions for your operation, visit:














Please log in to leave a comment.