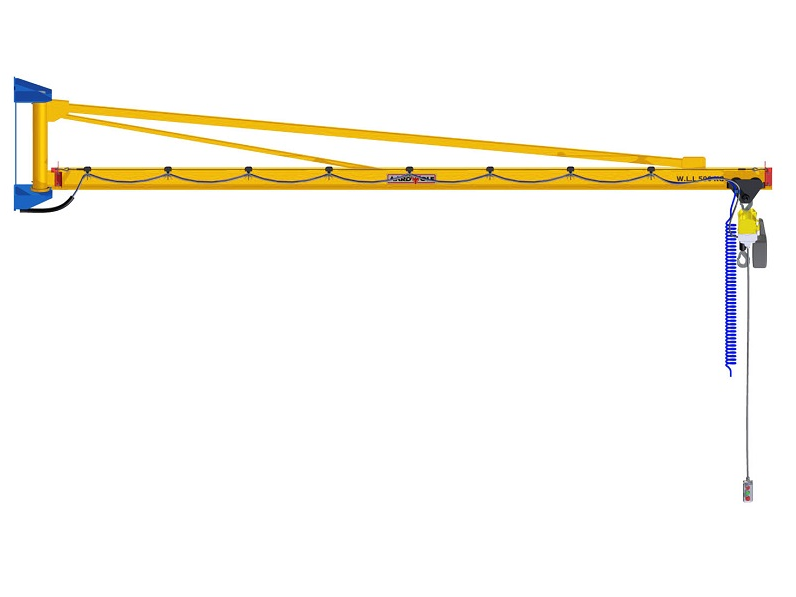
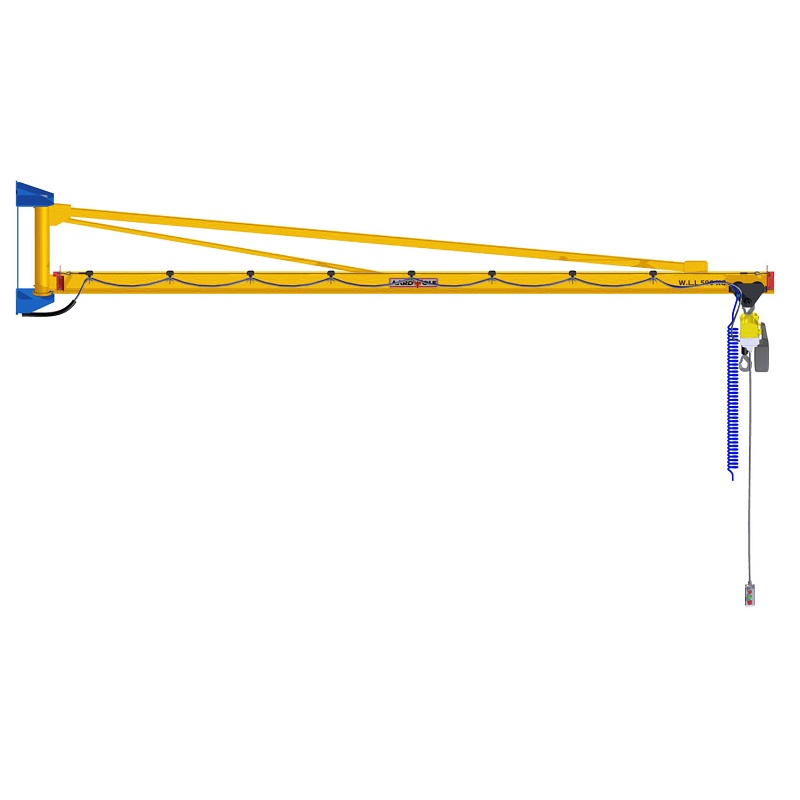
Jib crane Installation is more than a mechanical task—it’s a legal and safety obligation. Whether it’s a freestanding jib crane, wall-mounted jib crane, or articulating jib crane, the system must meet stringent regulatory standards to ensure workplace safety, operational reliability, and legal compliance.
This comprehensive guide explores the OSHA and ANSI standards for jib crane installation, integrating real-world experience, deep technical expertise, and certified authoritativeness to help contractors, facility managers, and safety officers understand what’s required from start to finish.
🧩 First, check if your location is ready: Jib Crane Installation Requirements for Your Facility
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Jib Crane Installation Standards Matter
A poorly installed jib crane can lead to:
- Structural failure
- Equipment damage
- Operator injury
- Costly OSHA penalties
Adhering to OSHA 1910 and ANSI/ASME B30.11/B30.17 standards isn’t just about compliance—it’s about ensuring that your equipment performs safely under real-world industrial loads.
Key Standards for Jib Crane Installation
1. OSHA Regulations
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets baseline safety standards for all crane installations in the U.S.
Relevant OSHA Sections:
- OSHA 1910.179 – Covers overhead and gantry cranes but sets expectations for all fixed-position lifting devices.
- OSHA 1910.184 – Regulates slings and rigging accessories used with jib cranes.
- OSHA 1910 Subpart N – General materials handling standards applicable to jib cranes.
2. ANSI/ASME Standards
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) provide technical guidelines.
Key Standards:
- ASME B30.11 – Monorails and underhung cranes (often used with jib setups)
- ASME B30.17 – Cranes for industrial use, including electric hoists
- ASME B30.2 – Overhead and gantry cranes; used as a reference for jib configurations
- ASME B30.20 – Below-the-hook lifting devices
Design & Load Requirements in Jib Crane Installation
Load Rating
- The crane must be permanently marked with its safe working load (SWL).
- Rated load must match the structure’s bearing capacity—both floor and wall.
Structural Engineering Review
For mast-type jib cranes, the ceiling and floor must bear axial and radial loads. A structural engineer should evaluate the:
- Concrete compressive strength (usually ≥ 3000 psi)
- Column support (for wall-mounted installations)
- Anchorage and bracing (especially in mast mounted jib cranes)
✅ Follow recommended configurations found in Jib Crane Installation Checklist for Contractors & Teams
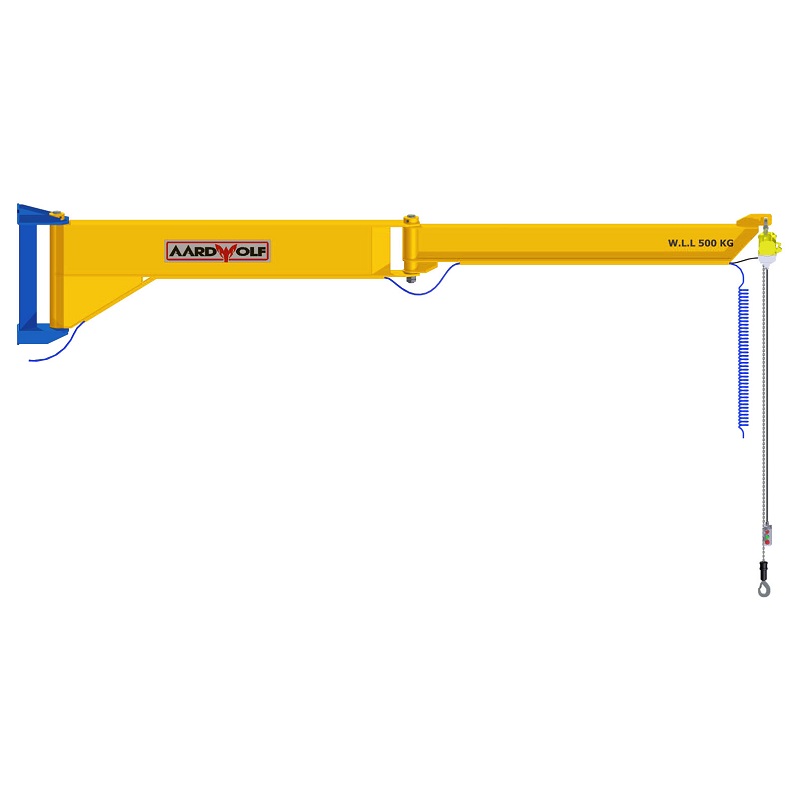
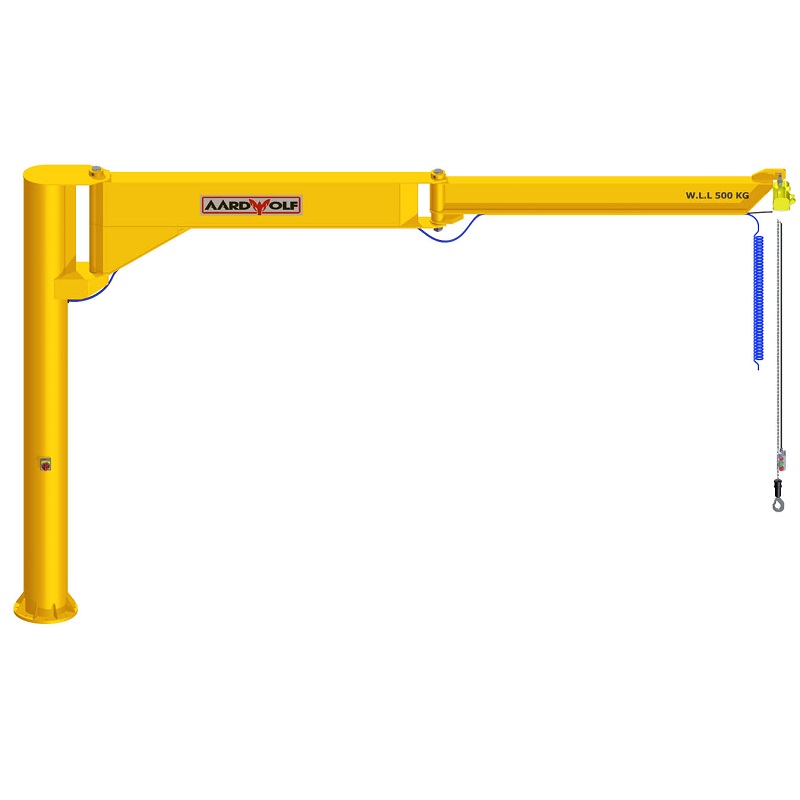
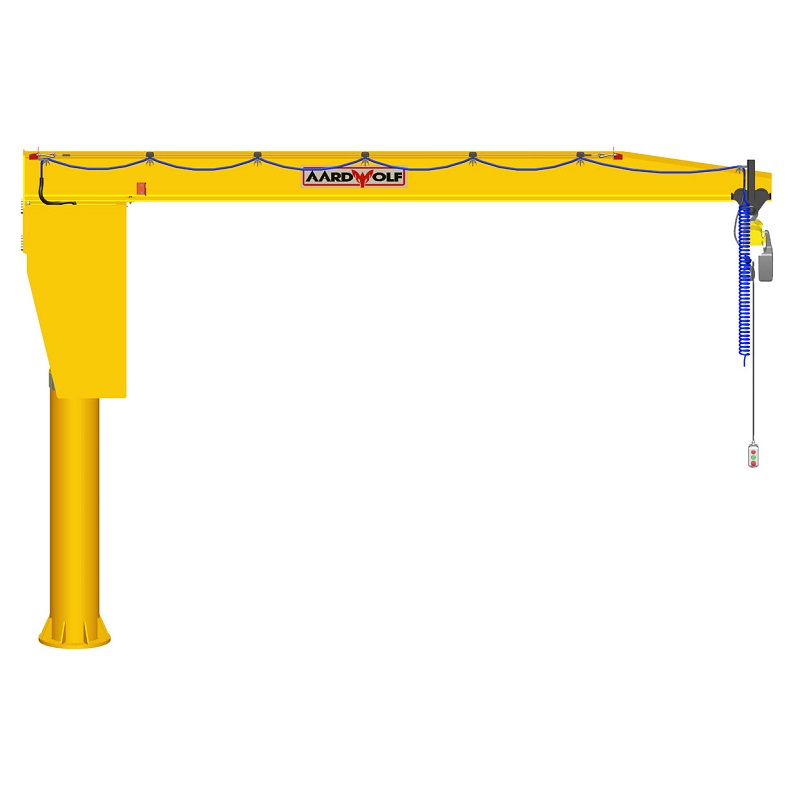
OSHA & ANSI Requirements by Jib Crane Type
| Jib Crane Type | OSHA/ANSI Highlights |
|---|---|
| Freestanding Jib Crane | Must meet base foundation specs and use certified anchors (see ASME B30.17) |
| Wall-Mounted Jib Crane | Requires certified mounting to load-bearing walls or columns with through-bolting |
| Mast-Type Jib Crane | Ceiling and floor structures must be verified; braces must meet ASME B30.2 standards |
| Articulating Jib Crane | Must maintain proper arm alignment, mobility zones, and anti-collision clearances |
Electrical Safety Standards
If your jib crane uses an electric hoist, it must comply with:
- NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code) – Grounding, circuit capacity, protection
- OSHA 1910.305 – Wiring methods for industrial equipment
- ASME B30.17 – Electric hoist power feeds and pendant control safety
Ensure all electrical work is performed by licensed electricians and inspected before commissioning.
Jib Crane Installation Process According to Standards
1. Site Inspection and Prep
- Assess site clearance and headroom
- Verify structural integrity of floor/wall
- Prepare anchor bolt layout using a certified template
2. Mechanical Installation
- Use calibrated torque wrenches for bolt tightening
- Mount hoist/trolley per manufacturer specs
- Maintain vertical mast alignment within 1/16 inch
Detailed process here: Jib Crane Installation Process: From Prep to Testing
3. Load Testing
- Static Test: Lift and hold 100% of rated capacity for 10 minutes
- Dynamic Test: Move load along full swing and trolley range
- Tests must be certified by a qualified person per ASME B30.17
Documentation & Certification
Your installation must be documented with:
- Load test results
- Foundation inspection report
- Electrical and mechanical checklists
- Operator manual and maintenance plan
- Warning labels and load capacity signage
Store all records for OSHA or insurance audits.
Common Non-Compliance Issues
| Issue | Risk |
|---|---|
| Inadequate anchoring | Structural failure during load movement |
| Wall not load-rated | Pullout of bolts or collapse |
| Electrical wiring violations | Shock hazard, fire risk |
| No load test performed | Voids warranty and violates OSHA policy |
| Missing documentation | Delays in inspection or insurance claims |
Avoid these: Jib Crane Installation Requirements for Your Facility
Maintenance & Ongoing Compliance
ANSI and OSHA both require routine inspections:
- Daily – Visual check by operator
- Monthly – Bolt torque, boom swing, hoist condition
- Annually – Full load test and structural review
Maintain a written log and schedule preventive maintenance to extend crane lifespan.
Final Thoughts: Safety First, Always
A jib crane is only as strong as its weakest installation link. By following OSHA and ANSI standards, you not only protect your workers but also safeguard your business from liability.
Whether you’re working with a mast-type jib crane, a freestanding system, or a wall-mounted solution, safety and compliance must lead every decision.
✅ Shop safe and certified: for more jib crane products
Further Reading & Resources:
- Jib Crane Installation Requirements for Your Facility
- Jib Crane Installation Checklist for Contractors & Teams
- Jib Crane Installation Process: From Prep to Testing
Install legally. Operate safely. Maintain confidently. That’s the standard for every jib crane.















Please log in to leave a comment.