Handling granite countertops is one of the most challenging material handling tasks in the stone fabrication and construction industries. Granite slabs are heavy, bulky, fragile, and expensive—requiring the use of specialized material handling equipment to ensure safety, efficiency, and damage prevention.
This article offers a comprehensive guide on how to improve material handling for granite countertops, drawing on best practices, modern technologies, and essential safety standards for workshop and jobsite operations.
🔗 How to Improve Material Handling for Granite Countertops?

Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Is Granite Handling So Complex?
Granite slabs typically weigh between 800 to 1,200 pounds and can reach lengths over 10 feet. They are susceptible to:
- Chipping and cracking during lifting or loading
- Injury risks due to improper handling
- High costs if damaged in transit or fabrication
Therefore, selecting the right industrial material handling solutions and training staff accordingly is essential.
Best Material Handling Equipment for Granite Countertops
1. Slab Lifters
Specialized slab lifters are designed to grip granite securely without damaging the surface. They are essential for workshops, factories, and distribution centers.
These lifters:
- Automatically clamp and release
- Handle slabs of varying thickness
- Reduce manual effort and injury risk
2. Vacuum Lifters
Vacuum lifters use suction pads to lift granite slabs with minimal contact. They’re ideal for polished surfaces and reduce the risk of scratching or damage.
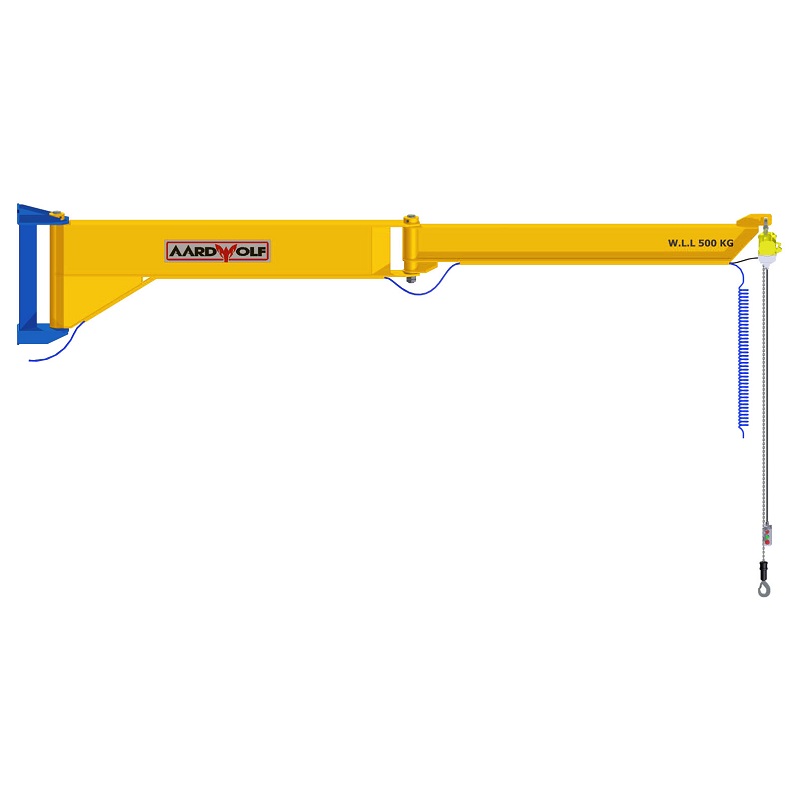
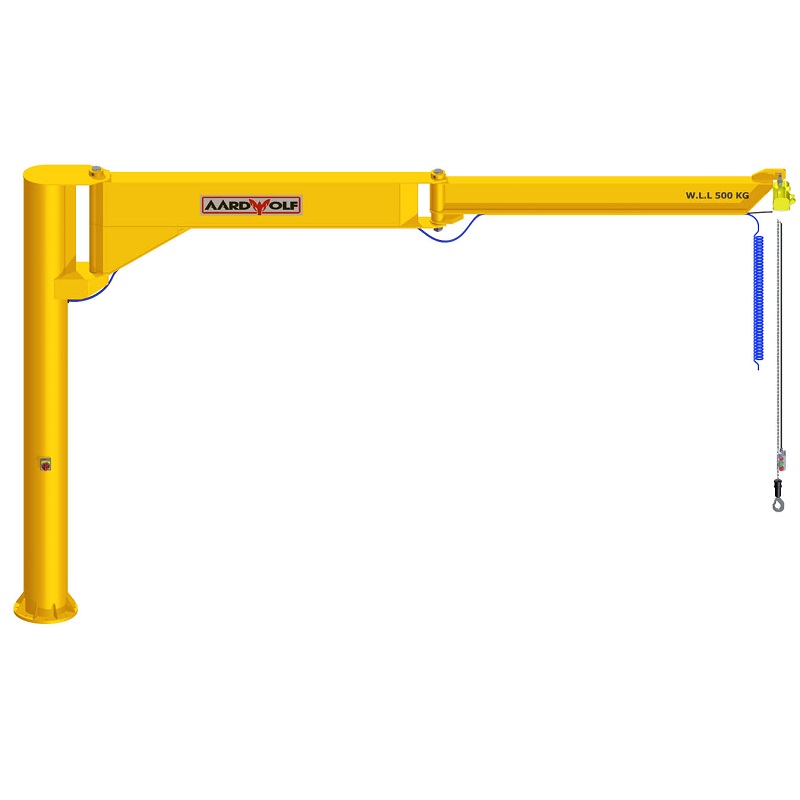
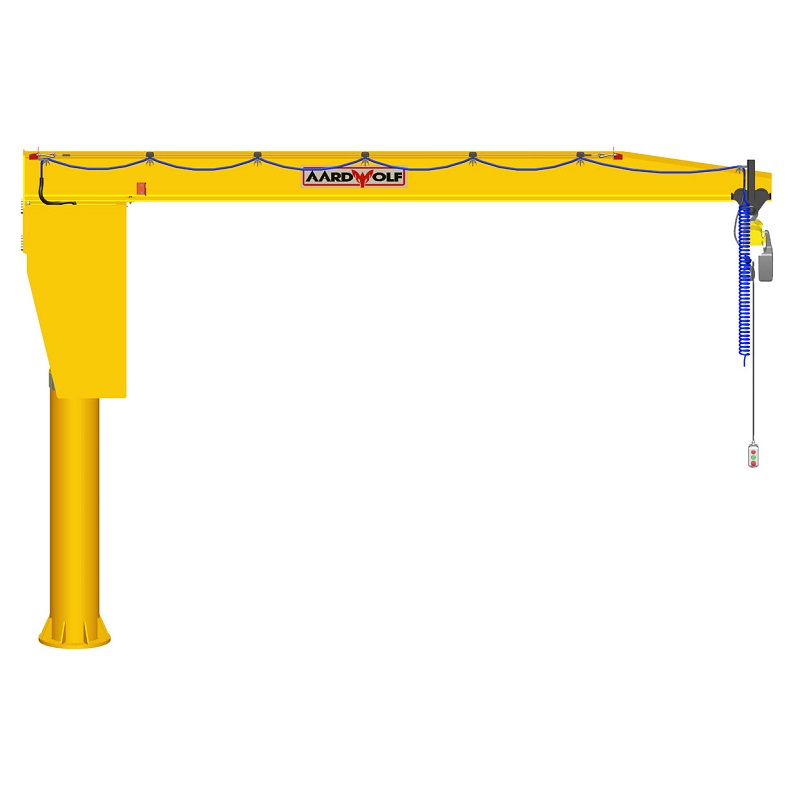
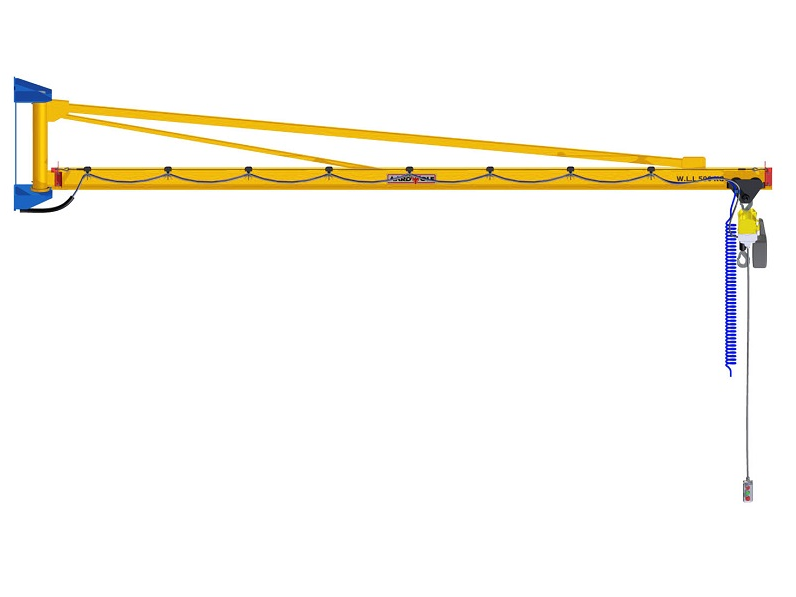
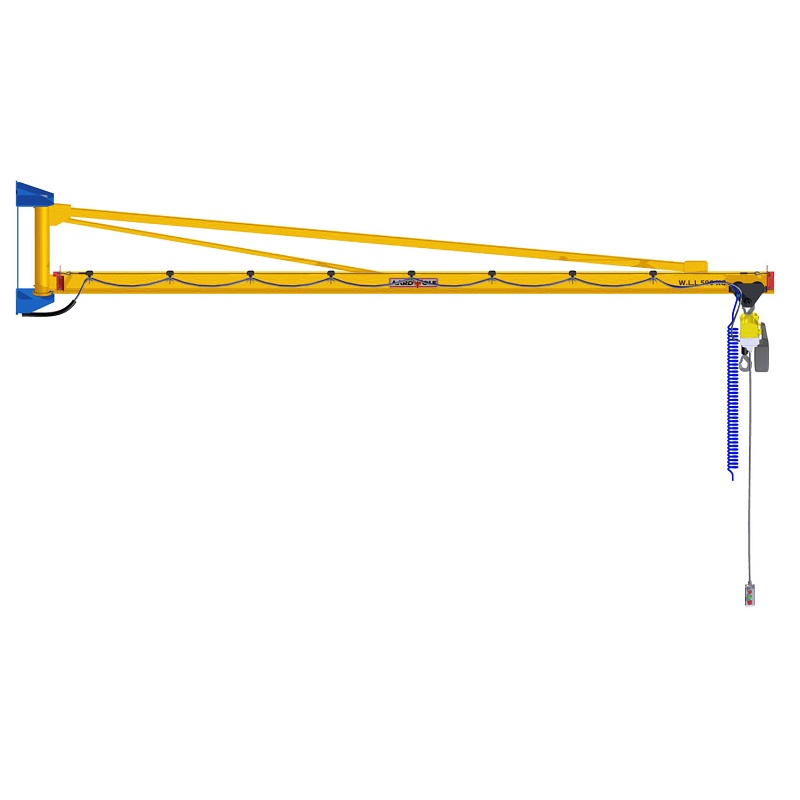
3. Jib Cranes
A jib crane enables overhead lifting in confined workshop spaces, rotating slabs to desired angles for cutting or polishing.
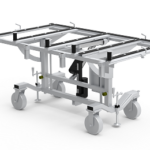
4. Paver Lifters for Outdoor Handling
For onsite granite countertop installations, paver lifters provide stable grip and easy transport.
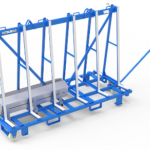
5. Material Handling Carts and Trolleys
Granite slab trolleys enable horizontal movement within the workshop and assist in staging materials for fabrication or shipping.
Facility Design and System Integration
Improving granite material handling goes beyond tools—it involves smart material handling system design considerations. This includes:
- Overhead systems to free up floor space
- Workstations designed for ergonomic access
- Integrated conveyors for material handling when dealing with smaller stone sections
- Defined paths for forklifts for material handling
Optimizing workflow reduces travel time, boosts productivity, and minimizes handling repetitions.
Automating Granite Handling
While granite is traditionally handled manually, there are now advanced automated material handling systems that assist in:
- Sorting slabs based on size and type
- Transporting slabs via robotic arms or rails
- Synchronizing slab movements with CNC cutting machines
🔍 Benefits of Automated Material Handling Systems:
- Reduced labor costs
- Higher accuracy
- Fewer human errors
- Faster throughput
Warehouse and Storage Solutions
Efficient warehouse material handling equipment prevents granite slab breakage and improves retrieval speed. Use:
- Vertical slab storage racks with safety clamps
- A-frame carts for secure slab transport
- Steel shelving with padded contact points
These are especially useful in material handling for warehouses and material handling for manufacturing stone products.
Manual Handling: Still Relevant?
In smaller workshops or job sites, manual material handling tools are still widely used. However, safety becomes a major concern.
🔗 Loose Clothing Is Best to Wear When Handling Material?
Safety Tips for Manual Material Handling:
- Always lift with multiple people
- Use gloves with non-slip grip
- Never wear loose clothing around moving machinery
- Store slabs upright and secure them to prevent tipping
Training and Compliance
Investing in material handling training programs ensures that employees understand how to:
- Use lifting equipment safely
- Avoid injury when working with heavy stone
- Follow correct procedures for rigging and hoisting
- Comply with material handling safety standards
Reducing Costs While Improving Handling
You don’t need a million-dollar system to improve granite handling. Consider these low-cost material handling solutions for small businesses:
- Purchase used material handling equipment for sale
- Rent tools for short-term projects
- Choose multi-functional devices that can lift and transport
- Work with reputable material handling equipment manufacturers for reliable solutions
Industry-Specific Considerations
🏗 Material Handling in Construction
Transport granite slabs securely to construction sites using paver lifters, forklifts, and padded racks.
🧱 Material Handling in Manufacturing
Granite countertops are typically finished in factories—requiring overhead systems, slab rotators, and CNC integration.
🛒 Material Handling in Logistics
Use secure, labeled packaging and padded shipping containers for distribution to retail or project sites.
Final Thoughts: How to Improve Material Handling for Granite Countertops
Improving material handling for granite countertops means combining the right tools, thoughtful workflow design, and proper training to ensure safety, reduce damage, and maximize productivity.
To summarize:
- Use specialized equipment like vacuum lifters, jib cranes, and slab lifters
- Automate repetitive handling processes where possible
- Train your workforce and maintain compliance with handling standards
- Design your facility for flow, space, and safety
🔗 How to Improve Material Handling for Granite Countertops?














Please log in to leave a comment.