In high-mix, high-velocity facilities, materials rarely move in straight lines. Machines, racking, and workers compete for space, and the cost of a delayed lift ripples across the entire schedule. That’s why modern jib crane components—from the boom and slewing assembly to the hoist, trolley, controls, and end effectors—are engineered with one unifying goal: turn every motion into productive motion. This article breaks down how each component is purpose-built for speed, precision, ergonomics, and safety, and how smart selection and upkeep translate directly into ROI.
New to component selection? Start with Why Choosing the Right Jib Crane Components Matters Most for the big-picture framework.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Efficiency Equation: What It Means for Jib Crane Components
Operational efficiency isn’t only about faster lifts. It’s a blend of:
- Cycle time (lift, travel, rotate, set)
- Placement accuracy (first-time-right)
- Operator effort (ergonomics, fatigue)
- Downtime avoidance (reliability, quick service)
- Floor-space yield (coverage per square meter)
Modern jib crane components are designed to improve each factor without compromising safety. The hallmark of a well-engineered system is smooth, predictable movement with minimal wasted effort.
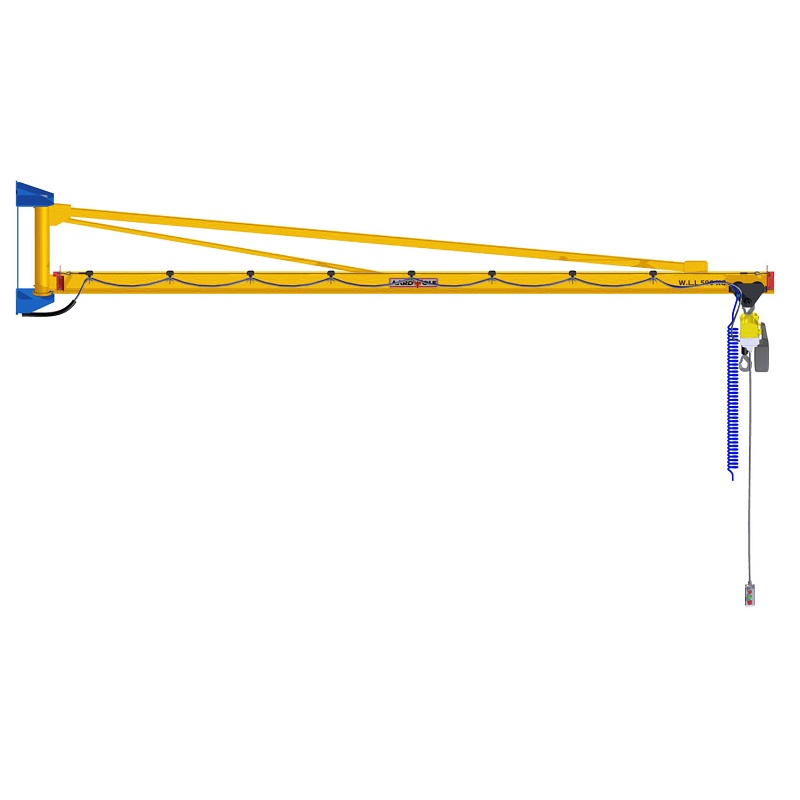
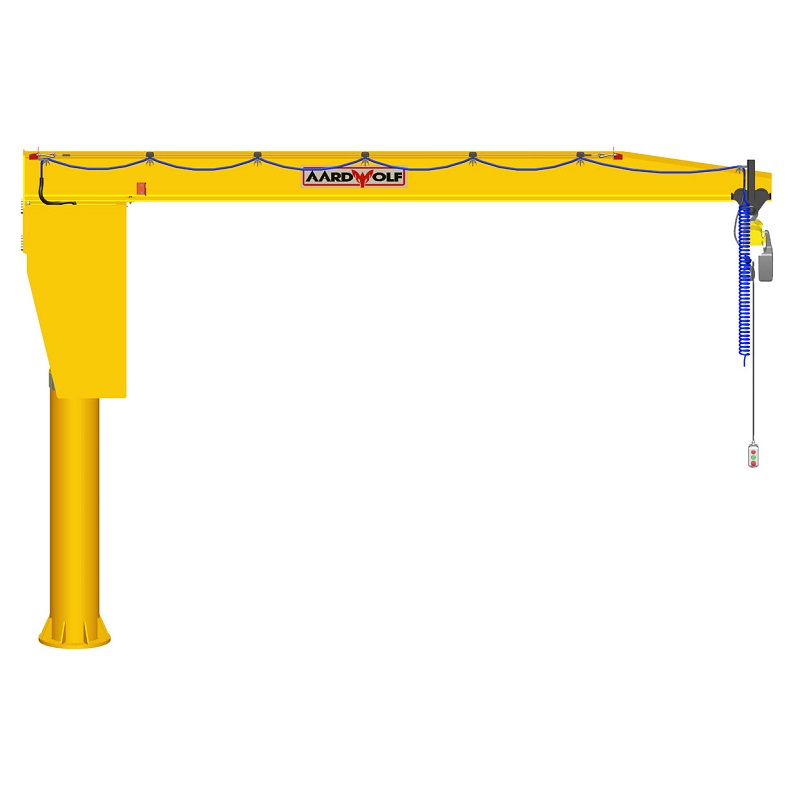
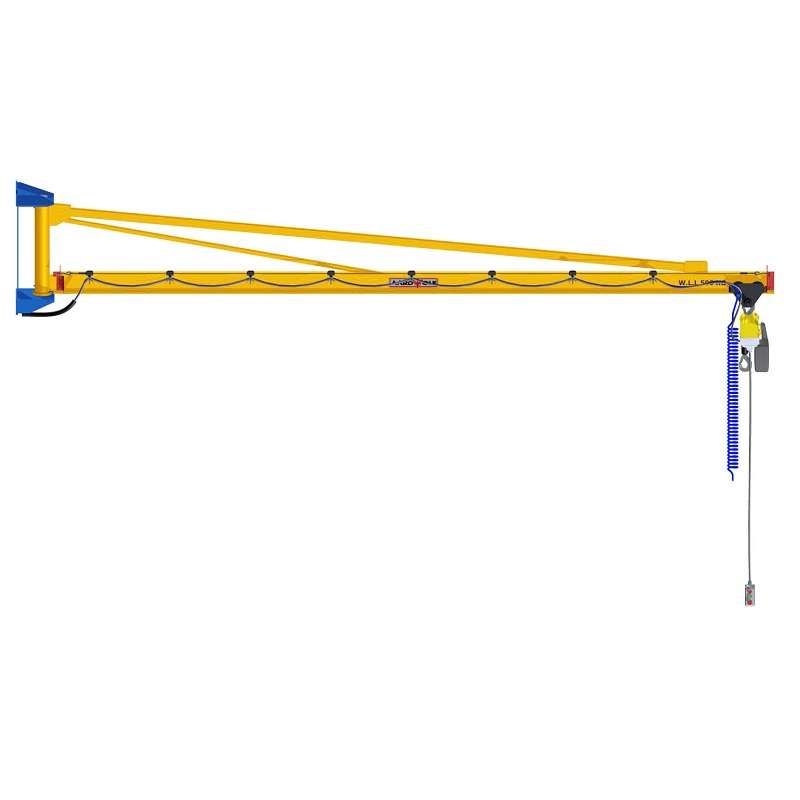
1) Boom & Geometry: Designing Reach Without Penalty
What’s new and why it matters
- Optimized section profiles (I-beam, box, or articulated segments) minimize deflection while preserving headroom. Less deflection means tighter placements and less time waiting for load sway to settle.
- Articulated booms add a “joint” for knuckle-like motion, letting operators move around pillars and machines without side-pulling. This reduces non-productive repositioning.
Efficiency impact
- Shorter approach distances and fewer corrective moves
- Cleaner hook paths, lowering collision and rework risks
Where it shines
- Tight cells, CNC islands, packing stations, and assembly lines. If you’re weaving between obstacles, a wall-mounted articulated model is often a game-changer: Articulated Jib Crane – Wall Mounted.
2) Slewing/Rotation Systems: Smooth Starts, Predictable Stops
Engineering focus
- Low-friction bearings or slewing rings limit startup force, making fine rotations easy—even under load.
- VFD-powered slewing (where fitted) enables soft start/stop, reducing load swing and operator strain.
- Mechanical and programmable stops protect equipment and define safe work zones.
Efficiency payoff
- Faster, more accurate lineups at the set-down point
- Less time waiting for sway to dampen
- Reduced micro-corrections that tire operators and consume cycle time
3) Trolleys: Low Headroom, Low Resistance, High Control
Design details that matter
- Precision wheel profiles matched to the beam reduce rolling resistance and rail wear.
- Sealed bearings cut maintenance and keep rolling friction consistent over time.
- Low-headroom architectures reclaim precious lift height in retrofit spaces.
Efficiency payoff
- Quicker, smoother horizontal travel with less push force
- Consistent alignment, which improves hook centering and placement accuracy
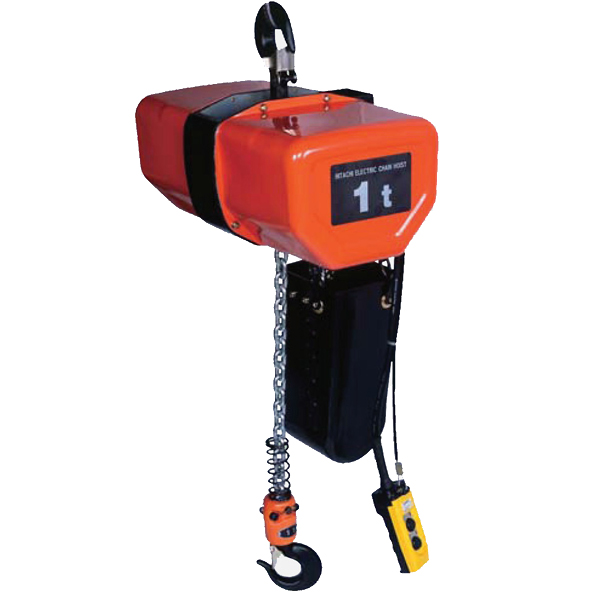
4) Hoists: Duty-Class Matched Power With Gentle Handling
Modern features
- Dual-speed or VFD-controlled electric chain/wire rope hoists for gentle acceleration and accurate inching.
- Thermal protection and load monitoring to prevent misuse and shorten diagnostics.
- High-cycles-per-hour duty classes to match real workloads—no more overheating after lunch rush.
Efficiency payoff
- Less rework from hard stops and jerky lifts
- Higher throughput without overheated motors or nuisance trips
- Faster, precise landings that protect delicate surfaces
5) Controls & Power Feed: Ergonomics = Speed + Safety
Control evolutions
- Radio remotes free the operator from pendant cable routing around obstacles, improving line-of-sight and eliminating snags.
- Pendant designs with positive-feedback buttons reduce mis-triggers and speed up repetitive motions.
Power and cable management
- Festoons, energy chains, or slip rings are selected to match motion profiles, preventing cable fatigue and unplanned stoppages.
Efficiency payoff
- Operators move with the load, not against the cord—reducing lost time and strain
- Fewer interruptions from cable damage or entanglement
6) End Effectors: The Last Inch of Efficiency
The fastest crane is still slow if it struggles to grip, protect, or release the load. Purpose-built tools close that gap:
- Vacuum lifters distribute forces evenly, protect finishes, and align panels precisely. For modular glass or sheet handling, see the Vacuum lifter.
- Clamps and magnets accelerate picks for stone, metal, and block products, cutting time lost to slinging.
- Forklift integration with a forklift boom turns mobile equipment into a versatile partner, streamlining inter-bay transfers so the jib crane focuses on precision placement.
Efficiency payoff
- Fewer drops and surface damage (less rework)
- Faster “hook-to-secure” time
- Safer, cleaner releases at the set point
7) Safety Devices: Built-In Speed Through Certainty
It sounds counterintuitive, but better safety is faster. When operators trust the gear, they move decisively.
- Overload protection prevents risky stalls and damage.
- Upper/lower limit switches shorten cycles by letting operators approach stops confidently.
- Emergency stops and interlocks protect people and uptime—issues are contained before they cascade.
For inspection and compliance planning, read What Role Do Jib Crane Components Play in Safety Checks?.
How Component Design Choices Reduce Total Cost to Lift (TCTL)
TCTL—your real cost per successful lift—drops when the crane does more with less operator effort, fewer corrections, and fewer breakdowns. Smart jib crane components influence:
- Energy use: VFDs and low-friction rolling gear reduce electrical and human energy.
- Consumables: Correct wheel/rail pairing and sealed bearings last longer.
- Unplanned downtime: Protective stops, load monitoring, and robust anchors stop small issues from becoming big ones.
- Training time: Intuitive controls and predictable motion shorten onboarding.
Spec to Win: A Practical Selection Checklist
Copy/paste this into your RFQ worksheet:
- Capacity & Duty
- Rated for peak load + 15–20% buffer
- Hoist duty class matched to cycles/hour and shifts/day
- Coverage & Geometry
- Reach, under-boom clearance, hook path
- Consider articulated geometry for obstacle-rich cells
- Slewing Assembly
- Manual vs. powered with VFD soft start/stop
- Mechanical stops and, if applicable, programmable rotation limits
- Trolley
- Wheel profile to match beam; sealed bearings
- Low-headroom option if height is tight
- Hoist
- Dual-speed or VFD; brake capacity; thermal protection
- Load display or overload monitoring for smarter decisions
- Controls & Power Feed
- Pendant vs. radio remote; interference testing
- Festoon/energy chain/slip ring—sized for motion and cycles
- End Effectors
- Task-specific: Vacuum lifter for panels, clamps/magnets for solids
- Quick-change interfaces if you handle multiple load types
- Anchorage/Structure
- Verified slab thickness, base plate, grout spec, torque sequence
- For wall-mounted, confirm building steel capacity
- Serviceability
- Access to grease points and panels; recommended spares kit
- Clear maintenance intervals and documentation
Best-Practice Use: Turning Design Into Day-1 Results
- Zero side-pull policy. Protect slewing bearings, trolleys, and hooks—this single practice extends life across the board.
- Smooth-lift technique. Use dual-speed/VFD features for gentle starts and landings; your cycle times will still drop as rework and sway disappear.
- Line-of-sight placement. Favor radio controls so operators can watch the load and landing zone directly.
- Dedicated end effectors. Don’t force generic hooks to do specialist work—use a vacuum tool for panels or a clamp for stone/blocks.
- Integrate mobile handling. A forklift boom helps with distance moves; the jib crane focuses on precision work at the station.
Maintenance for Sustained Efficiency
Even the best engineering needs simple, regular care:
Daily (operator): Visual check (hook, chain/rope, pads), quick function test (up/down, trolley, slew, limits, E-stop).
Monthly (technician): Track cleaning, trolley wheel/axle inspection, brake gap check, festoon/energy chain travel, torque sample on anchors.
Quarterly: Slew backlash measurement, gearbox oil sample (if applicable), pendant/radio inspection and battery routine.
Annually: Load test/certification, NDT at boom/welds, overload calibration, insulation resistance testing; update service log with measurable values (deflection, backlash, chain elongation).
Spot early degradation patterns in What Common Issues Affect Jib Crane Components Over Time?.
Real-World Layouts: Where Efficiency Is Won
- Cell manufacturing: Articulated booms keep hook paths short and unobstructed; VFD hoists land parts right where they’re needed.
- Warehousing & docks: Low-headroom trolleys maximize hook height under mezzanines; radio control keeps operators clear of pinch points.
- Stone & glass shops: Application-specific end effectors—Vacuum lifter for panels, clamps for blocks—slash damage and speed cycle times.
When you need a compact, rotation-friendly solution that works in the tightest corners, look at Articulated Jib Crane – Wall Mounted, and explore more crane products to match your duty, space, and material mix.
FAQs: Efficiency-Centric Jib Crane Components
Q: Do VFD hoists really improve throughput?
A: Yes. Soft starts and controllable inching reduce sway and overshoot, so operators land loads faster and with fewer corrections—shorter overall cycles.
Q: We often work around machines—how do we avoid side pulls?
A: Choose articulated geometry or adjust layout so the hook path stays vertical. Program rotation limits and train operators in “smooth lift, smooth set” habits.
Q: Which end effector gives the biggest productivity bump?
A: For sheet/panel work, a Vacuum lifter typically delivers the largest gains because it shortens secure/release time and cuts damage-related rework.
Q: Can we combine forklifts and jib cranes efficiently?
A: Yes—use a forklift boom for transport between cells and the jib crane for precise placement. It reduces crane hours on long moves and keeps the crane focused on value-added handling.
The Bottom Line
Modern jib crane components are engineered to convert every inch of movement into productive output: stiff-but-light booms for accuracy, low-friction slewing for smooth rotation, precisely matched trolleys for effortless travel, VFD hoists for controlled lifts, ergonomic controls for line-of-sight work, and task-specific end effectors for fast, damage-free handling. When you pair the right components with disciplined use and maintenance, you’ll feel it in your metrics—shorter cycles, fewer injuries, less rework, and more good parts out the door.
For deeper planning, see:
- Why Choosing the Right Jib Crane Components Matters Most
- What Role Do Jib Crane Components Play in Safety Checks?
- What Common Issues Affect Jib Crane Components Over Time?
And when you’re ready to shortlist, explore more crane products and configure the package that’s purpose-built for your space, materials, and throughput.














Please log in to leave a comment.